Design overview: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Back to [[regbot | | Back to [[regbot | Regbot]] main page. | ||
==Design overview hardware== | ==Design overview hardware== | ||
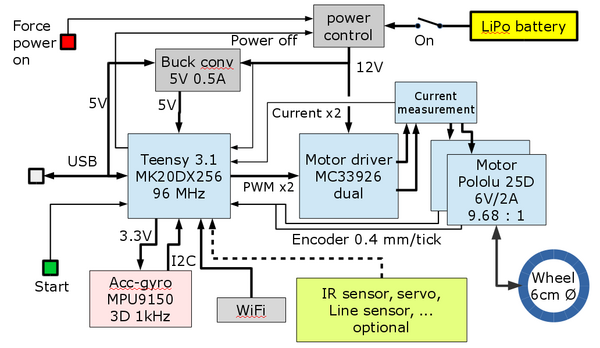
Regbot consist of a microprocessor board (teensy 3. | Regbot consist of a microprocessor board (teensy 3.2/3.5) that controls 2 motors (Pololu 25D) through a motor driver (MC33926). Motor rotation data is collected from motor encoders. Motor current is avaiable and there is further a gyro-accelerometer sensor (see figure 1 below). | ||
The processor is supplied with 5V from either USB or from a 12V battery or power supply. | The processor is supplied with 5V from either USB or from a 12V battery or power supply. | ||
A | A start button that starts a mission and a power button that enables power after a shutdown. | ||
The robot is differential controlled, where a difference in velocity between left and right wheel generates a turn. | The robot is differential controlled, where a difference in velocity between left and right wheel generates a turn. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Figure 1. Hardware blockdiagram. | Figure 1. Hardware blockdiagram. | ||
Most blocks are off-the-shelf hardware modules from PJRC (Teensy), Pololu (motor, driver and buck | Most blocks are off-the-shelf hardware modules from PJRC (Teensy), Pololu (motor, driver and buck converter) and Sparkfun 9150 (IMU). Some of the supported sensors are optional, but all will have gyro to enable balancing and most also wifi to enable monitoring and confuguration without a USB cable. | ||
Other sensors like an line (edge) detector (edge of a tape line on the floor), IR distance sensors (Sharp 2Y0A21 type) and wifi access may be implemented on some of the robots. | Other sensors like an line (edge) detector (edge of a tape line on the floor), IR distance sensors (Sharp 2Y0A21 type) and wifi access may be implemented on some of the robots. | ||
==Design | ==Design block diagram== | ||
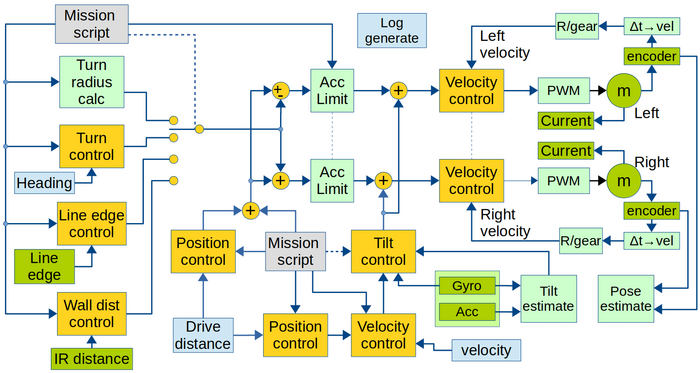
The robot | The robot data and control flow is shown as a block diagram in figure 2 below. | ||
[[File:blockdiagram_software.png|700px]] | [[File:blockdiagram_software.png|700px]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Figure 2. Overview of software data flow. Yellow is control blocks. | Figure 2. Overview of software data flow. Yellow is control blocks. | ||
Green is hardware (motor and sensors), Light green is calculations. Light blue is obtained values. | Green is hardware (motor and sensors), Light green is calculations. Light blue is obtained values. | ||
Gray is input values. | Gray is input values from mission. | ||
Sample time for all controllers and data values are 1ms. | Sample time for all controllers and data values are 1ms. | ||
All software is written in c++, based on Arduino libraries. | All software is written in c++, based on Arduino libraries. | ||
All controllers can be switched off. I.e. if the velocity controller is switched off then the motors will never run. To control the motor voltage (rather than the velocity) then configure the velocity controller vith Kp = 0 and feed forward Kf=1. | |||
* [[Design calculations]] | * [[Design calculations]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:39, 11 January 2021
Back to Regbot main page.
Design overview hardware
Regbot consist of a microprocessor board (teensy 3.2/3.5) that controls 2 motors (Pololu 25D) through a motor driver (MC33926). Motor rotation data is collected from motor encoders. Motor current is avaiable and there is further a gyro-accelerometer sensor (see figure 1 below).
The processor is supplied with 5V from either USB or from a 12V battery or power supply.
A start button that starts a mission and a power button that enables power after a shutdown.
The robot is differential controlled, where a difference in velocity between left and right wheel generates a turn.
The processor is an ARM MK20DX256 processoren (a 32bit 96MHz microprocessor) and is programmed to implement a number of control loops that is able to control some basic movements of the robot (see figure 2).
Figure 1. Hardware blockdiagram. Most blocks are off-the-shelf hardware modules from PJRC (Teensy), Pololu (motor, driver and buck converter) and Sparkfun 9150 (IMU). Some of the supported sensors are optional, but all will have gyro to enable balancing and most also wifi to enable monitoring and confuguration without a USB cable.
Other sensors like an line (edge) detector (edge of a tape line on the floor), IR distance sensors (Sharp 2Y0A21 type) and wifi access may be implemented on some of the robots.
Design block diagram
The robot data and control flow is shown as a block diagram in figure 2 below.
Figure 2. Overview of software data flow. Yellow is control blocks. Green is hardware (motor and sensors), Light green is calculations. Light blue is obtained values. Gray is input values from mission.
Sample time for all controllers and data values are 1ms. All software is written in c++, based on Arduino libraries.
All controllers can be switched off. I.e. if the velocity controller is switched off then the motors will never run. To control the motor voltage (rather than the velocity) then configure the velocity controller vith Kp = 0 and feed forward Kf=1.