Robobot bridge: Difference between revisions
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Robobot_bridge == | == Robobot_bridge == | ||
The robobot_bridge is a communication interface that handles communication between the clients and (most of) the robot hardware. | |||
Main features are: | |||
* Interface with REGBOT hardware (motors and sensors) | |||
* Interface with a gamepad (joystick) - e.g. manual control of the robot. | |||
* interface to a small display (8 lines each 20 characters). | |||
* interface to clients, e.g. REGBOT GUI and mission control application. | |||
[[File:robobot_bridge_blocks.png | 600px]] | [[File:robobot_bridge_blocks.png | 600px]] | ||
The Robobot_bridge | The Robobot_bridge links the low-level robot hardware REGBOT, the remote control gamepad and the minor status display. The display and gamepad are in the new version moved to Regbot. | ||
There are three interface modules - one for each of the interfaces | There are three interface modules - one for each of the interfaces; these handle direct communication with the device. | ||
The exchange format is always a line-oriented clear text. The gamepad generates a status line with all switches and axes and is input | The exchange format is always a line-oriented clear text. The gamepad generates a status line with all switches and axes and is input only. The REGBOT is already clear text line-oriented and communicates two ways - as two independent channels; in and out. | ||
=== | === Automatic start === | ||
Robobot_bridge is started from the startup script "start_bridge.sh", this script is called at reboot as a "Cron" job. | |||
- or started manually (is also better for debugging, as it has some on-line help (type help after start): | |||
sudo pkill bridge | |||
cd | |||
./bridge | |||
The command | ===Bridge command line=== | ||
The bridge command line (when started in a console) can issue commands and view the bridge's status. | |||
This feature is primarily for debugging. | |||
The bridge handles single-character commands: | |||
Robobot_bridge command-line commands: | Robobot_bridge command-line commands: | ||
| Line 29: | Line 46: | ||
# Robobot_bridge help: | # Robobot_bridge help: | ||
# Commands are all single line text | # Commands are all single-line text starting with a keyword | ||
# (up to 6 characters) followed by text or numbers: | # (up to 6 characters) followed by text or numbers: | ||
# Main topics: | # Main topics: | ||
# | # regbot Sends the rest of the line to the robot; see 'regbot help' for options | ||
# bridge See 'bridge help' for options | # bridge See 'bridge help' for options | ||
# client See 'client help' for options | # client See 'client help' for options | ||
# q quit | # q quit | ||
| Line 41: | Line 57: | ||
# All lines starting with '#' are assumed to be comments | # All lines starting with '#' are assumed to be comments | ||
# All commands are stored as a data item with a keyword as ID | # All commands are stored as a data item with a keyword as ID | ||
# All data items | # All data items have reserved subcommands, see: | ||
# item h Help for data item 'item' | # item h Help for data item 'item' | ||
The item help looks like: | |||
>>regbot:pose help | |||
# help for special second parameter: | |||
# get Gets the value of the data item | |||
# meta Gets 'key meta r name vs s name p description': r=responder, vs: 0=val 1=seq, s=source, p=priority | |||
# subscribe p Set subscription 0=none, -1=all updates, else interval in ms | |||
# onupdate p c Set onUpdate action 0=none, -1=all updates, else interval in ms; c=action string | |||
# status Shows status for the item (updates and subscribers) | |||
# name xxx Sets name or description for the data item | |||
# logopen Opens a (new) logfile and logs all updates with timestamp (key.txt) | |||
# logclose Closes logfile (if open) | |||
# help This help | |||
=== Handler === | === Handler === | ||
The handler receives line-oriented text messages, | The handler receives line-oriented text messages, starting with a text keyword or character. A number of parameters (text or numbers) and all space-separated terminated with a new-line character. | ||
An example message is | An example message is | ||
regbot:pose logopen | |||
This command starts logging the pose interface from the Regbot (to /home/local/log_20230202_102432.834/regbot_pose.txt) | |||
If this is the first time the command is handled, then a data item is created in the message database. A specific handler is found for this message type, and the message is stored, and the specific handler is notified. | |||
If the message type is handled before, then the data item is updated, and the specific handler is notified. | |||
If this is the first time the command is handled, then a data item is created in the message database. A specific handler is found for this message type and the message is stored and the specific handler notified. | |||
If the message type is handled before, then the data item is updated and the specific handler notified. | |||
=== Port server === | |||
The port server will open for connections on TCP/IP port 24001. | |||
The server will open a new client connection for each connection. Up to 20 clients can be served. | |||
All communication is in clear text and line-oriented. | |||
On connection, the bridge will send the following message | |||
# Welcome to REGBOT bridge - send 'help' for more info | |||
It will start with a '#' to indicate that this is just for information. | |||
All help text, other information, and debug messages will be sent starting with the '#' character as the first character. | |||
Sending a 'client help' will return the special socket server help: | |||
# Socket server help: | |||
# list: Gives a list of active clients | |||
# help: This help text | |||
The command 'bridge sources' gives a list of data source devices; like this: | |||
>>bridge sources | |||
%% source list: is active, source:dev, [params]* | |||
source -4 ini:dev 1 has no data yet | |||
Hostname: Oscar | |||
source -3 bridge:dev 1 Oscar:24001 1 9 46.251 0 0 | |||
source -5 console:dev 1 has no data yet | |||
source -3 gamepad:dev 0 /dev/input/js0 0 0 0 0 0 | |||
source -1 ros:dev 1 has no data yet | |||
source -1 host:dev 1 has no data yet | |||
source -2 regbot:dev 1 /dev/ttyACM0 25751 0 158 0 0 | |||
source -2 ttyACM1:dev 0 /dev/ttyACM1 0 0 0 0 0 | |||
source 0 socket00:dev 0 has no data yet | |||
source 1 socket01:dev 0 has no data yet | |||
source 2 socket02:dev 1 has no data yet | |||
In this case 3 clients (source 0, 1 and 2) connection 3 (source 2) is still active. | |||
This function is intended to see if someone else - by accident - is fiddling with the robot. | |||
== Data logging == | |||
Logged files can be displayed in MATLAB using a script like this | |||
ir = load('log_irdist_20200105_133333.297.txt'); % | |||
h = figure(300) | |||
hold off | |||
plot(ir(:,1) - ir(1,1), ir(:,2)); | |||
hold on | |||
plot(ir(:,1) - ir(1,1), ir(:,3)); | |||
grid on | |||
grid MINOR | |||
axis([5,12,0,1]) | |||
legend('IR 1 distance', 'IR 2 distance','location','southwest') | |||
xlabel('sec') | |||
ylabel('distance [m]') | |||
saveas(h, 'ir1-ir2.png') | |||
The filename depends on the interface. | |||
The first column is the timestamp, and to avoid extremely high numbers on the time axes, the first-time value is subtracted from the plot. | |||
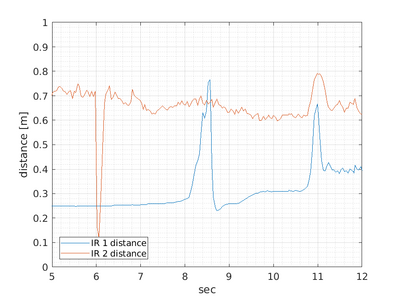
And in this case, the plot shows: | |||
[[File:ir1-ir2.png | 400px]] | |||
The plot shows longer distances (IR2) have more noise than shorter distances (IR1). | |||
In this case, the drive is started by an IR2 distance less than 0.3m (at 6 seconds); hereafter, the robot moves, and the IR 1 distance (looking right) sees different obstacles. | |||
Latest revision as of 13:12, 2 February 2023
Back to robobot
Robobot_bridge
The robobot_bridge is a communication interface that handles communication between the clients and (most of) the robot hardware.
Main features are:
- Interface with REGBOT hardware (motors and sensors)
- Interface with a gamepad (joystick) - e.g. manual control of the robot.
- interface to a small display (8 lines each 20 characters).
- interface to clients, e.g. REGBOT GUI and mission control application.
The Robobot_bridge links the low-level robot hardware REGBOT, the remote control gamepad and the minor status display. The display and gamepad are in the new version moved to Regbot.
There are three interface modules - one for each of the interfaces; these handle direct communication with the device. The exchange format is always a line-oriented clear text. The gamepad generates a status line with all switches and axes and is input only. The REGBOT is already clear text line-oriented and communicates two ways - as two independent channels; in and out.
Automatic start
Robobot_bridge is started from the startup script "start_bridge.sh", this script is called at reboot as a "Cron" job.
- or started manually (is also better for debugging, as it has some on-line help (type help after start):
sudo pkill bridge cd ./bridge
Bridge command line
The bridge command line (when started in a console) can issue commands and view the bridge's status. This feature is primarily for debugging.
The bridge handles single-character commands:
Robobot_bridge command-line commands: q: quit s: status of data items etc h: this help help: help for the bridge Lines with more than one character are sent to the handler as a message.
Longer commands are sent to the handler and merged with messages from any other command, and the 'help' command shows:
# Robobot_bridge help: # Commands are all single-line text starting with a keyword # (up to 6 characters) followed by text or numbers: # Main topics: # regbot Sends the rest of the line to the robot; see 'regbot help' for options # bridge See 'bridge help' for options # client See 'client help' for options # q quit # h Console help # help This help # All lines starting with '#' are assumed to be comments # All commands are stored as a data item with a keyword as ID # All data items have reserved subcommands, see: # item h Help for data item 'item'
The item help looks like:
>>regbot:pose help # help for special second parameter: # get Gets the value of the data item # meta Gets 'key meta r name vs s name p description': r=responder, vs: 0=val 1=seq, s=source, p=priority # subscribe p Set subscription 0=none, -1=all updates, else interval in ms # onupdate p c Set onUpdate action 0=none, -1=all updates, else interval in ms; c=action string # status Shows status for the item (updates and subscribers) # name xxx Sets name or description for the data item # logopen Opens a (new) logfile and logs all updates with timestamp (key.txt) # logclose Closes logfile (if open) # help This help
Handler
The handler receives line-oriented text messages, starting with a text keyword or character. A number of parameters (text or numbers) and all space-separated terminated with a new-line character.
An example message is
regbot:pose logopen
This command starts logging the pose interface from the Regbot (to /home/local/log_20230202_102432.834/regbot_pose.txt)
If this is the first time the command is handled, then a data item is created in the message database. A specific handler is found for this message type, and the message is stored, and the specific handler is notified. If the message type is handled before, then the data item is updated, and the specific handler is notified.
Port server
The port server will open for connections on TCP/IP port 24001.
The server will open a new client connection for each connection. Up to 20 clients can be served.
All communication is in clear text and line-oriented. On connection, the bridge will send the following message
# Welcome to REGBOT bridge - send 'help' for more info
It will start with a '#' to indicate that this is just for information. All help text, other information, and debug messages will be sent starting with the '#' character as the first character.
Sending a 'client help' will return the special socket server help:
# Socket server help: # list: Gives a list of active clients # help: This help text
The command 'bridge sources' gives a list of data source devices; like this:
>>bridge sources
%% source list: is active, source:dev, [params]* source -4 ini:dev 1 has no data yet Hostname: Oscar source -3 bridge:dev 1 Oscar:24001 1 9 46.251 0 0 source -5 console:dev 1 has no data yet source -3 gamepad:dev 0 /dev/input/js0 0 0 0 0 0 source -1 ros:dev 1 has no data yet source -1 host:dev 1 has no data yet source -2 regbot:dev 1 /dev/ttyACM0 25751 0 158 0 0 source -2 ttyACM1:dev 0 /dev/ttyACM1 0 0 0 0 0 source 0 socket00:dev 0 has no data yet source 1 socket01:dev 0 has no data yet source 2 socket02:dev 1 has no data yet
In this case 3 clients (source 0, 1 and 2) connection 3 (source 2) is still active.
This function is intended to see if someone else - by accident - is fiddling with the robot.
Data logging
Logged files can be displayed in MATLAB using a script like this
ir = load('log_irdist_20200105_133333.297.txt'); %
h = figure(300)
hold off
plot(ir(:,1) - ir(1,1), ir(:,2));
hold on
plot(ir(:,1) - ir(1,1), ir(:,3));
grid on
grid MINOR
axis([5,12,0,1])
legend('IR 1 distance', 'IR 2 distance','location','southwest')
xlabel('sec')
ylabel('distance [m]')
saveas(h, 'ir1-ir2.png')
The filename depends on the interface. The first column is the timestamp, and to avoid extremely high numbers on the time axes, the first-time value is subtracted from the plot. And in this case, the plot shows:
The plot shows longer distances (IR2) have more noise than shorter distances (IR1). In this case, the drive is started by an IR2 distance less than 0.3m (at 6 seconds); hereafter, the robot moves, and the IR 1 distance (looking right) sees different obstacles.