Flexbot design: Difference between revisions
From Rsewiki
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* An angled DC motor to control the wheel. | * An angled DC motor to control the wheel. | ||
* Two linear actuators to control the motion of the robot's body. | * Two linear actuators to control the motion of the robot's body. | ||
Each of these actuators is controlled by a μ-processor board (Teensy 3.2). The Teensy controls the actuators | Each of these actuators is controlled by a μ-processor board (Teensy 3.2). The Teensy controls the actuators via a motor driver and receives feedback from the actuators encoder signals. | ||
Each leg is split up in two parts which are presented as the [[#Lower leg hardware design|lower leg]] and the [[#Upper leg hardware design|upper leg]]. | |||
==Lower leg hardware design== | |||
The lower leg configuration includes: | |||
* Angled DC motor to run the wheel - model IG42-CRGM | |||
* SyRen 10 motor driver | |||
* Teensy 3.2 μ-processor board | |||
* Pololu 24V to 5V voltage regulator - model D24V22F5 | |||
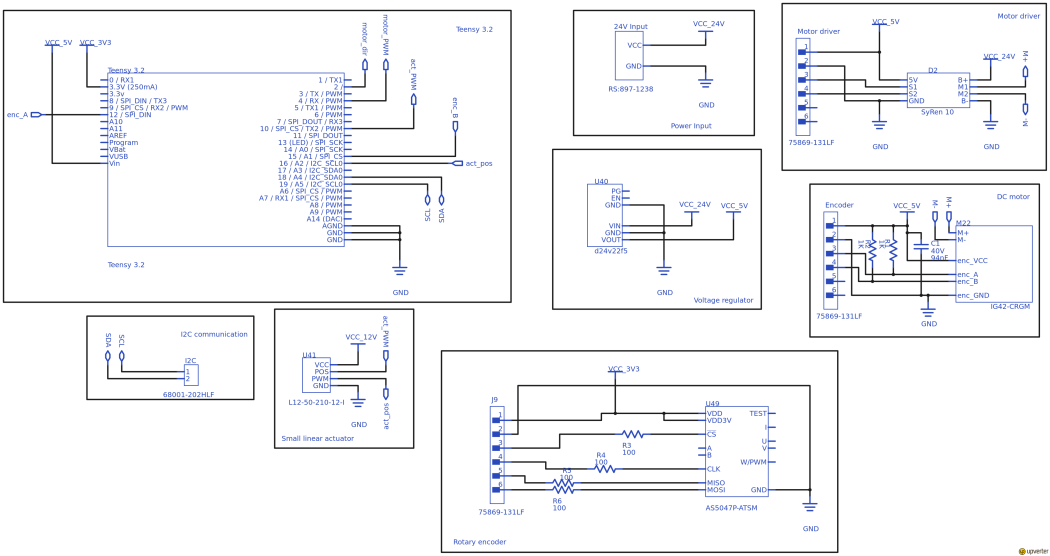
Figure 1: | The schematic for the lower leg is shown in Figure 1 and can be forked and edited using the free online e-CAD design tool Upverter. Link to the project on Upverter is given [https://upverter.com/DTUAutomationControlFlexbot/97591cdad92a1840/Teensy_Wheel_Configuration/ here]. | ||
[[File:Teensy Wheel Configuration.png|1050px]] | |||
Figure 1: Schematic for the lower leg for the Flexbot. | |||
==Upper leg hardware design== | |||
Revision as of 08:34, 3 July 2017
Back to Flexbot main page
Design overview hardware
Each "leg" of the flexbot consists of 3 actuators.
- An angled DC motor to control the wheel.
- Two linear actuators to control the motion of the robot's body.
Each of these actuators is controlled by a μ-processor board (Teensy 3.2). The Teensy controls the actuators via a motor driver and receives feedback from the actuators encoder signals. Each leg is split up in two parts which are presented as the lower leg and the upper leg.
Lower leg hardware design
The lower leg configuration includes:
- Angled DC motor to run the wheel - model IG42-CRGM
- SyRen 10 motor driver
- Teensy 3.2 μ-processor board
- Pololu 24V to 5V voltage regulator - model D24V22F5
The schematic for the lower leg is shown in Figure 1 and can be forked and edited using the free online e-CAD design tool Upverter. Link to the project on Upverter is given here.
Figure 1: Schematic for the lower leg for the Flexbot.