Variables: Difference between revisions
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
* Data type "t" A time value (implemented as a double). | * Data type "t" A time value (implemented as a double). | ||
* Data type "s" in a string variable, but is not implemented yet. | * Data type "s" in a string variable, but is not implemented yet. | ||
===Access variables by name=== | |||
Varables in other resource modules are accessed using their name, like: | Varables in other resource modules are accessed using their name, like: | ||
Revision as of 07:53, 15 February 2009
Most resource modules will include some configuration or result variables, that should be available form other modules or from an external interface - a configuration file or a operator interface.
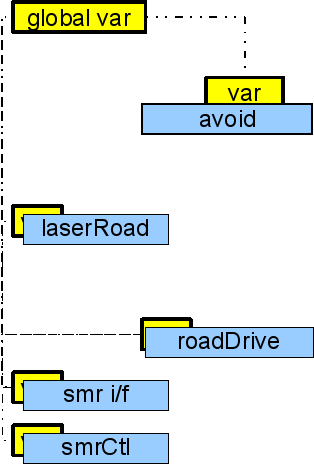
var pool
The var-pool is a method of sharing variable values between different modules. This figure is used to illustrate that the 'RoadDrive' module needs data from 'LaserRoad' for road data and access to the 'avoid' module for obstacle avoidance services, and finally to the robot real time control server. Each module is compiled without need for any header files from the other modules.
This inter module communication is handled by the var-pool function inherited into all resources.
The var-pool (loaded by module load=var) is the variable root. Each resource act as a structure and the local variables in each resource belong to this structure. so:
smr.speed
is defined by the resource 'smr' as a variable with the name 'speed'.
Define variables and methods
A resources may define a number of local variables and functions, like this roadDrive resource:
void UResRoadDrive::createBaseVar()
{
//
addVar("version", getResVersion() / 100.0, "d", "Resource version");
varUpdateTime = addVar("updateTime", 0.0, "t", "Last time the road drive command was calles");
varEdgeDist = addVar("edgeDist", 0.35, "d", "Nominel distance to road edge");
varFwdDist = addVar("forwardDist", 6.0, "d", "Exit-pose distance from robot");
varEdge = addVar("edge", 0.0, "d", "Reference edge 0=left, 1=top, 2 = right");
varTgtPose = vp->addVar("tgtX", "5.0 0.0 0.0", "pose", "Array with target position
used in obstacle avoidance (set by call)");
...
// and methods
addMethod("left", "d", "Follow left side at this distance");
addMethod("right", "d", "Follow left right at this distance");
addMethod("top", "d", "Follow road center at this distance");
addMethod("target", "sd", "get target pose with this reference, the 's' (string)
parameter may be either 'left', 'right', or 'top',
the 'd' parameter is the desired distance from the
reference line (positive is left)");
...
}
Access variables
Variables are added to the system by the 'addVar' call, giving a variable name, an initial value, a type ('d' for double) and a description of the variable (the description is a help to the operator, when inspecting or setting values).
The addVar(.) method returns a pointer to a UVariable type, this is used when locally accessing the variable, e.g.:
d = varFwdDist->getValue();
x = varTgtPose->getValue(0); // get first value in the pose array
varTgtPose->setValued(-0.3, 1); // Set the pose y value (index 1)
varTgtPose->setValued("2.2 -0.3 0.0"); // Set all values in one call - note that the values are set as a string.
varTgtPose->setPose(pPose); // Set all values from a pointer to a UPose structure
The implemented data types are
- Data type "d" an array of doubles (may have one element only, and then used without an index)
- Data type "pose" is an array of 3 double values (index 0, 1, 2 for x, y, th)
- Data type "3D" is an array of 3 values (index 0, 1, 2 for X, Y, and Z)
- Data type "rot" is an array of 3 values describing a 3D rotation, index 0 is Omega (X-axis), index 1 is Phi (y-axis) and index 2 is Kappa (z-axis)
- Data type "dq" is two values is describing a data value and a quality.
- Data type "t" A time value (implemented as a double).
- Data type "s" in a string variable, but is not implemented yet.
Access variables by name
Varables in other resource modules are accessed using their name, like:
vp = getVarPool(); // vp is of the type UVarPool *
isOK = vp->getValue("smr.speed", &vel);
isOK &= vp->getValue("odopose.pose[1]", &y); // gets the current odometry pose Y-value
The value name is using a dot-notation for the module owner - the resource name - followed by a dot and the variable name. If variable is an array, then an index may be added. If the variable exist - both resource and variable - the function returns 'true' and the double sized value is returned at the adress supplied as the second parameter. Sub-structures may be created locally with a 'vp->addStructLocal("name", "help text")' if needed. Sub structures can not be arrays.
Use variable update as an event
A variable structure may be used to trigger events. An event may be defined by a client with a command like:
>> varPush struct=smr cmd="var smr.allcopy"
If this is the case a flag will be set if one (or more) of the variables defined in the 'smr' resource is updated. The command will then be executed by the server thread at first opportunity.
Methods
Methods are defined by a name and a parameter list. They must be announced to the var-pool by an 'addMethod' call, like these from above:
addMethod("left", "d", "Follow left side at this distance");
addMethod("right", "d", "Follow left right at this distance");
addMethod("top", "d", "Follow road center at this distance");
addMethod("target", "sd", "get target pose with this reference, the 's' parameter may be either 'left', 'right', or 'top', the 'd' parameter is the desired distance from the reference line (positive is left)");
The parameters are the object implementing the call - typically 'this' will do, the name, the parameter list and a textual description. The parameter list may hold a combination of 'd' (double), 's' (string) and 'c' (class) as in-parameters.
Implement method
The implementation of the method must implemented in the resource function named methodCall:
bool UResRoadDrive::methodCall(const char * name, const char * paramOrder, char ** strings, double * pars,
double * value, UDataBase ** returnStruct, int * returnStructCnt)
{
bool result = true;
if ((strcasecmp(name, "road") == 0) and (strcmp(paramOrder, "sd") == 0))
*value = driveRoad(strings[0], pars[0]);
else if ((strcasecmp(name, "left") == 0) and (strcmp(paramOrder, "d") == 0))
*value = driveSide(0, pars[0], 0);
else if ((strcasecmp(name, "top") == 0) and (strcmp(paramOrder, "d") == 0))
*value = driveSide(1, pars[0], 0);
else if ((strcasecmp(name, "right") == 0) and (strcmp(paramOrder, "d") == 0))
*value = driveSide(2, pars[0], 0);
else if (...)
...
else
result = false;
return result;
}
The function is called by the var-pool module, and the function must determine which of the defined methods that are called. If the method is not implemented, then the function should return 'false'. As can be seen from the code, the function names are not intended to be case sensitive, and the parameter list is tested too, so the same method name may be used with different parameter lists. The parameters in the call are, after the name and the parameter list, the three types of parameters and the return value, in the following order:
- 'strings' a string array with as many elements as there is s' parameters in the parameter list.
- 'pars' a double array with as many elements as there is 'd' parameters in the parameter list.
- 'value' is where the primary result of the function is to be returned. If the method result is expressed in a double then here is the place to return the value. If the reply is a more complex, then this value could be used to flag success (1.0) or failure (0.0).
- 'returnStruct' is an array of pointers to a structure buffer. This may also be used as an input parameter, with as many pointers in the array as there is 'c' parameters in the parameter list.
- 'returnStructCnt' is a count of the number of available pointers in the 'returnStruct' array. On return this value must be changed to the actual number of class values returned. If the pointer array actually points at structures, then the method is expected to copy the relevant data to the provided buffer. If the pointer array (its first element) points to NULL, then the method is expected to return a pointer to a (one or more) structure in its own memory space. The receiver is then responsible for using the data before it is changed.
The return structures must be defined as a class inherited from the base class 'UDataBase'. The following types are p.t. defined in this way:
- UDataDouble - holds just a double value
- UDataString - holds a c-string
- UPosition - holds an x,y,z value
- UPosRot - a 3D pose of e.g. a camera or a laser scanner on a robot
- ULine - holds a line (3D with 2D support) definition (3D point and 3D (unit) vector)
- ULineSegment - same as line, but with a length.
- UMatrix - the basic matrix class
- UMatrix4 - a 4x4 (or less) matrix for 2 or 3D calculations.
- UPolygon - a sequence of UPositions to form a poly-line or a polygon.
- UObstacleGroup - a group of UPolygon obstacles.
- UPose - a 2D pose (x,y,h) - and from this UPoseT (with time) UPoseVel (with velocity)
- UManSeq - a sequence of manoeuvres to get from one pose to another
Method call
A call to a method in another module could look like this:
{
const int MPC = 4; // parameter count
double pars[MPC], v;
char * driver = (const char *)"roadDriver";
UManSeq * manNew = NULL;
bool isOK;
int n = 1;
...
pars[0] = exitPose.x;
pars[1] = exitPose.y;
pars[2] = exitPose.h;
pars[3] = vel;
isOK = call("avoid.getAvoidPath", "dddd", NULL, pars, &v, (UDataBase**) &manNew, &n);
if (isOK and v == 1.0)
// supply manoeuvre sequence to smr interface resource
isOK = call("smrCtl.setPlan", "sc", &driver, NULL, &v, (UDataBase**) &manNew, &n);
...
}
Where the first call just supplies an double array with 4 elements and expect a pointer to a manoeuvre sequence in return. If the call was a success the return value 'v' will be 1.0, and then the received manoeuvre sequence is send to the smr interface module. This call has a string and a class as parameters. The unused parameter pointers are set to NULL.