Drone control: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Build on a hand-wired PCB as a prototype | Build on a hand-wired PCB as a prototype | ||
[[Drone control hardware]] | [[Drone control hardware]] | ||
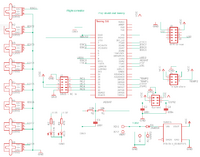
[[File:schematic_rev0.png | 200px]] | |||
== Drone software == | == Drone software == | ||
Revision as of 08:12, 10 October 2020
Drone project
This project is intended to be a rather simple core drone stabilizer application based on Teensy and the prop shield.
Intended to be expanded with an outer control loop with a non-realtime sensor, e.g. GNSS, camera or laser scanner.
Hardware
Build on a hand-wired PCB as a prototype
Drone software
Propeller - motor performance
Motor test app
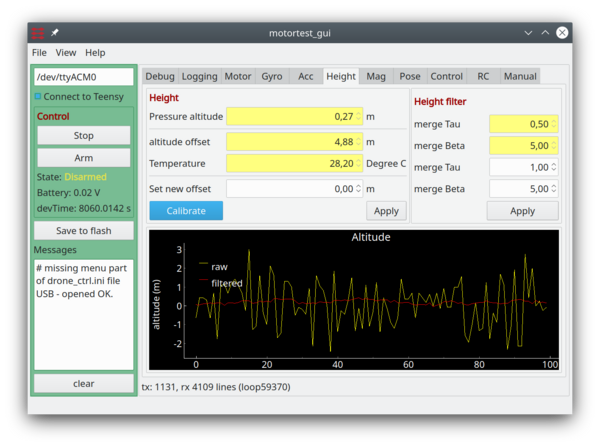
A motor test GUI is available (in the motortest_gui directory) - it will talk to the motortest firmware - and there is no need for the prop-shield for this application.
Motor test GUI. There is the possibility to log time performance (in the log tab), to test run an ESC (or up to 6 ESCs) in the data tab.
The hardware configuration and pin-out are described in the hardware section above.
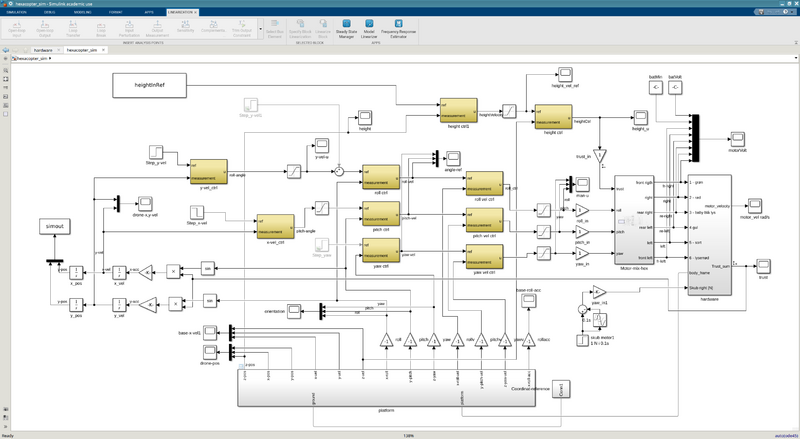
MATLAB simulation
Once the drone hardware (mass, configuration, motor and propeller) is known, then it can be simulated in Matlab simulink. The script in the doc/matlab directory has scrips for the simulation and estimating a linear transfer function in an operating point and calculate the needed controller parameters (roll, pitch, yaw - velocity and position as well as height control).
Further controllers for lateral velocity are added too, but these last controllers are not included in the drone firmware.
Simulink model of hexacopter.
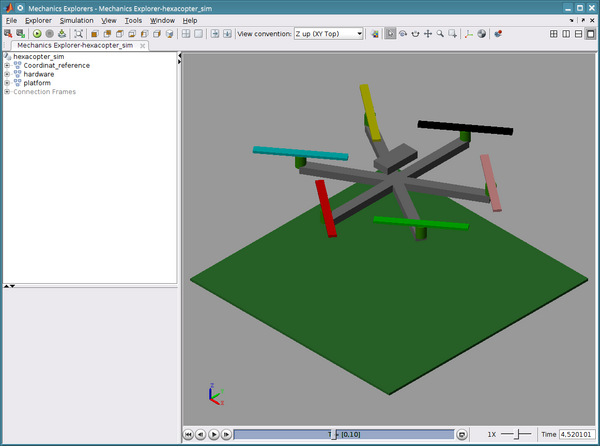
Sim mechanics simulated hex-drone hoovering.