Serial port handling: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Back to [[Basebot]] | Back to [[Basebot]] | ||
== | == Basebot data == | ||
Basebot data needs to be saved into a file to make it usable for MATLAB. | |||
A log is available after a basebot run. | |||
E.g. by typing ''start'' in the monitor area or by pressing the ''start' button on the robot itself. | |||
The logfile will be sent when the mission is complete, or alternatively by sending the command ''log'' to the robot. | |||
== Arduino IDE == | |||
I couldn't find a way to save the serial monitor data to a disk file. | I couldn't find a way to save the serial monitor data to a disk file. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 16: | ||
So find another app that allows communication in the serial line and save the output to a disk file (or allow copy-paste to do the same). | So find another app that allows communication in the serial line and save the output to a disk file (or allow copy-paste to do the same). | ||
== Visual Studio Code == | |||
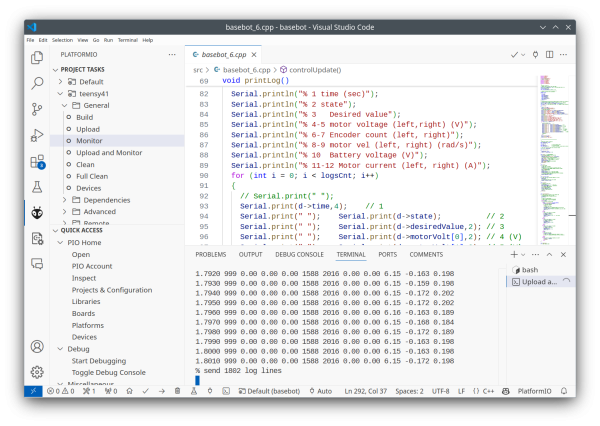
In the monitor area the log data is shown (e.g. after typing ''log''), like: | |||
[[file: VS-Code-data-from-monitor.png | 600px]] | |||
The data received in the monitor area will be saved to a ''logs'' directory on the ''basebot'' directory. | |||
In VS Code, use the explorer to open the ''logs'' directory and find the newest logfile: | |||
[[file: VS-Code-data-from-monitor-file.png | 600px]] | |||
The saved file could look like this: | |||
( | % log | ||
% Basebot log for Aya | |||
% Sample time 1000 us, Gear 9.60, Wheels 0.03 m, PPR 48 | |||
% maximum log samples 8333 each sized 48 bytes | |||
% 1 time (sec) | |||
% 2 state | |||
% 3 Desired value | |||
% 4-5 motor voltage (left,right) (V) | |||
% 6-7 Encoder count (left, right) | |||
% 8-9 motor vel (left, right) (rad/s) | |||
% 10 Battery voltage (V) | |||
% 11-12 Motor current (left, right) (A) | |||
0.0000 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.23 -0.163 0.202 | |||
0.0010 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.168 0.202 | |||
0.0020 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.163 0.193 | |||
0.0030 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.163 0.198 | |||
0.0040 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.168 0.189 | |||
0.0050 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.159 0.179 | |||
0.0060 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.159 0.179 | |||
... | |||
1.7960 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.16 -0.163 0.189 | |||
1.7970 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.168 0.184 | |||
1.7980 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.172 0.189 | |||
1.7990 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.163 0.198 | |||
1.8000 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.163 0.198 | |||
1.8010 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.172 0.198 | |||
% send 1802 log lines | |||
All the lines starting with '%' will be ignored by MATLAB. Here is especially the explanation of the data columns. | |||
The file can be loaded into MATLAB by | |||
dd01 = load('device-monitor-250830-174925.log'); | |||
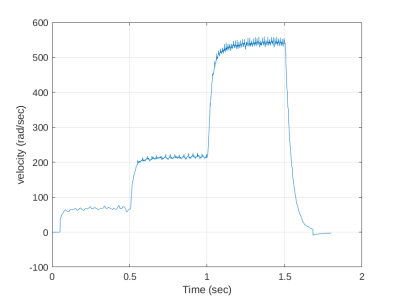
And plotter by e.g.: | |||
h = figure; | |||
plot(dd01(:,1), dd01(:,8)) | |||
grid on | |||
xlabel('Time (sec)') | |||
ylabel('velocity (rad/sec)') | |||
saveas(h, 'plot-of-logfile.png'); | |||
Giving | |||
[[file:plot-of-logfile.png | 400px]] | |||
== Linux == | == Linux == | ||
Latest revision as of 07:45, 31 August 2025
Back to Basebot
Basebot data
Basebot data needs to be saved into a file to make it usable for MATLAB.
A log is available after a basebot run. E.g. by typing start in the monitor area or by pressing the start' button on the robot itself.
The logfile will be sent when the mission is complete, or alternatively by sending the command log to the robot.
Arduino IDE
I couldn't find a way to save the serial monitor data to a disk file.
So find another app that allows communication in the serial line and save the output to a disk file (or allow copy-paste to do the same).
Visual Studio Code
In the monitor area the log data is shown (e.g. after typing log), like:
The data received in the monitor area will be saved to a logs directory on the basebot directory.
In VS Code, use the explorer to open the logs directory and find the newest logfile:
The saved file could look like this:
% log % Basebot log for Aya % Sample time 1000 us, Gear 9.60, Wheels 0.03 m, PPR 48 % maximum log samples 8333 each sized 48 bytes % 1 time (sec) % 2 state % 3 Desired value % 4-5 motor voltage (left,right) (V) % 6-7 Encoder count (left, right) % 8-9 motor vel (left, right) (rad/s) % 10 Battery voltage (V) % 11-12 Motor current (left, right) (A) 0.0000 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.23 -0.163 0.202 0.0010 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.168 0.202 0.0020 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.163 0.193 0.0030 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.163 0.198 0.0040 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.168 0.189 0.0050 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.159 0.179 0.0060 10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0 0.00 0.00 6.22 -0.159 0.179 ... 1.7960 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.16 -0.163 0.189 1.7970 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.168 0.184 1.7980 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.172 0.189 1.7990 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.163 0.198 1.8000 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.163 0.198 1.8010 999 0.00 0.00 0.00 1588 2016 0.00 0.00 6.15 -0.172 0.198 % send 1802 log lines
All the lines starting with '%' will be ignored by MATLAB. Here is especially the explanation of the data columns.
The file can be loaded into MATLAB by
dd01 = load('device-monitor-250830-174925.log');
And plotter by e.g.:
h = figure;
plot(dd01(:,1), dd01(:,8))
grid on
xlabel('Time (sec)')
ylabel('velocity (rad/sec)')
saveas(h, 'plot-of-logfile.png');
Giving
Linux
In Linux, the serial device is called /dev/ttyACM0 (typically), and to copy the robot output to a file is:
$ cat /dev/ttyACM0 > aaa.txt
And use ctrl-C to stop.
You can, in another terminal, send commands to the robot, i.e.:
$ echo "start" > /dev/ttyACM0
This is the same as pressing the start button.
Apple
I don't know