Ricbot: Difference between revisions
| Line 315: | Line 315: | ||
' | ' | ||
--- | --- | ||
The data is: timestamp (host), timestamp Teensy, Teensy ID, version, battery voltage, ... (the rest depend on the platform). | |||
Revision as of 08:54, 18 January 2026
Ricbot, a wheeled sensor platform
Ricbot is intended for fast deployment to areas of interest.
Main features:
- Reused motors and wheels from an old "Elector Wheelie" platform
- Designed to fit into a normal car for deployment, i.e can be disassembled to no more than 55cm in height.
- No more than 25-30 kg, requiring 1 or 2 persons to load or unload.
- Wheel-odometry recording (and timestamped)
- Camera image recording (and timestamped), the intention is Realsense D435.
- Maybe GNSS recording too.
- Manual remote control.
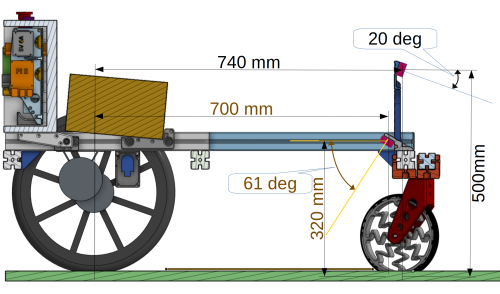
Tentative layout:
Length is 1m, free height 25cm, width 65cm.
Installation notes
Camera position
Forward-looking camera: Intel RealSense D455, FOV 87 x 58 deg, range 0.6 to 6m.
Down-looking camera: Intel RealSense D435, FOV: 87 x 58 deg, range 0.3 to 3m.
Cabling
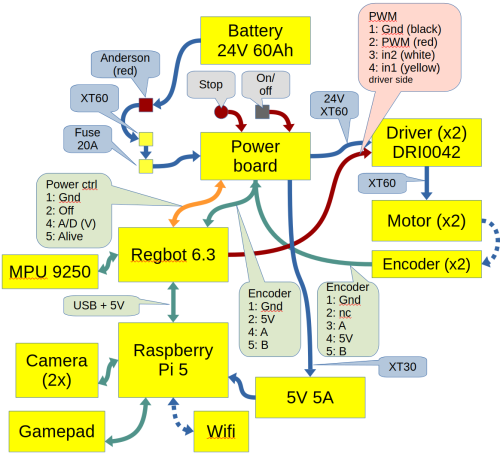
DRI0042: https://wiki.dfrobot.com/15A_Single_DC_Motor_Driver_SKU__DRI0042
Regbot 6.3: Regbot hardware board
5V 5A: | Aliexpress link to device
DRI0042 to Regbot 4-pin PWM
DRI Regbot PWM Software 7 GND (black) 1 GND -- 4 PWM (red) 2 in1 PIN_xxxx_DIR 5 IN1 (white) 3 in2 PIN_xxxx_PWM 6 IN2 (yellow) 4 fault PIN_xxxx_FAULT 3 5V out
DRI0042 control values IN1 IN2 PWM OUT1, OUT2 Motor Behavior 0 0 x Stop 1 1 x Vacant (relax) 1 0 1 Forward 100% 0 1 1 Reverse 100% 1 0 PWM Forward at PWM speed 0 1 PWM Reverse at PWM speed
Power control
Pin IDC10-pin Software Function 1 (black) 1 -- GND 2 (red) 3 LS_1 (pin 27) power off (when low) -- pt not working (wrong mod on power board) 3 (white) 4 LS_0 (A6) battery voltage (39k/4.7k) 4 (yellow) 6 LS_4 (pin 26) Alive LED
Intel RealSense
Install
sudo apt-get install automake libtool libusb-1.0-0-dev libx11-dev xorg-dev libglu1-mesa-dev sudo apt install libssl-dev
Library and examples
cd ~/git git clone https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense.git cd librealsense mkdir build cd build cmake .. make -j3 sudo make install
Copy udev rules to udev
cd ~/git/librealsense/config/99-realsense*.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/ udevadm control --reload-rules
All example commands start with rs-, e.g.:
rs-capture rs-pointcloud
Teensy interface
The Teensy interface implements a bridge to MQTT, a motor controller (velocity and turn rate), and a remote control.
The configuration is in
/home/local/svn/teensy_interface/build/robot.ini
See also Robobot teensy interface.
Start at boot
See the similar start setup in [[1]].
Comment out (or delete) the start of the camera streamer (not compatible with RealSense 3D cam)
Install software on Raspberry Pi
Perform the same installation as Robobot install on Raspberry, except for the serial port configuration (which should not be needed).
Teensy software
This is the Regbot software, configured to match the Ricbot.
See more details here Regbot firmware.
Intel Librealsense
Installing support for Intel librealsense.
sudo apt install libssl-dev sudo apt-get install freeglut3-dev sudo apt-get install xorg-dev cd git git clone https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense.git cd librealsense mkdir build cd build cmake ..
I also needed to install libusb-1.0-0-dev
sudo apt install libusb-1.0-0-dev
This path was not included in the CMakeLists.txt, so I added this line at the beginning of the CMakeLists.txt:
cd librealsense nano CMakeLists.txt
add
include_directories( /usr/include/libusb-1.0/ )
like here:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
set( LRS_TARGET realsense2 )
project( ${LRS_TARGET} LANGUAGES CXX C )
# Allow librealsense2 and all of the nested project to include the main repo folder
set(REPO_ROOT ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR})
include_directories(${REPO_ROOT})
include_directories( /usr/include/libusb-1.0/ )
include(CMake/lrs_options.cmake)
include(CMake/connectivity_check.cmake)
...
ROS2
From https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/Installation/Ubuntu-Install-Debs.html
Install
export ROS_APT_SOURCE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/ros-infrastructure/ros-apt-source/releases/latest | grep -F "tag_name" | awk -F\" '{print $4}')
curl -L -o /tmp/ros2-apt-source.deb "https://github.com/ros-infrastructure/ros-apt-source/releases/download/${ROS_APT_SOURCE_VERSION}/ros2-apt-source_${ROS_APT_SOURCE_VERSION}.$(. /etc/os-release && echo ${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-${VERSION_CODENAME}})_all.deb"
sudo dpkg -i /tmp/ros2-apt-source.deb
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ros-dev-tools
Install full ROS2 Jazzy
sudo apt install ros-jazzy-desktop
Start in this ROS2 environment, now and in new terminals:
source /opt/ros/jazzy/setup.bash echo "source /opt/ros/jazzy/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=0 echo "export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=0" >> ~/.bashrc
Install ROS QT GUI stuff
sudo apt install '~nros-jazzy-rqt*'
Create workspace
From https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/Tutorials/Beginner-Client-Libraries/Colcon-Tutorial.html
Install colcon
sudo apt install python3-colcon-common-extensions
Create workspace directory
mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src cd ~/ros2_ws
From within this directory clone (any) standard package
e.g. tutorial examples
git clone https://github.com/ros2/examples src/examples -b jazzy
Build the examples; this is memory and CPU-hungry, so the option --executor sequential may come in handy, especially on a Raspberry Pi, but it will take significantly longer.
colcon build --symlink-install --executor sequential
Allow use of colcon_cd
echo "source /usr/share/colcon_cd/function/colcon_cd.sh" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export _colcon_cd_root=/opt/ros/jazzy/" >> ~/.bashrc
To use the mixin shortcut for some colcon options, add:
colcon mixin add default https://raw.githubusercontent.com/colcon/colcon-mixin-repository/master/index.yaml colcon mixin update default
MQTT client
The un-modified mqtt_client package can act as a bridge between the teensy_interface and the ROS domain.
From MQTT to ROS, the translation is using the primitive ROS type string for the parameters of the teensy_interface messages. The MQTT topic name is translated to ROS topic names as specified in the parameter file below.
From ROS to Teensy, the message should be published on a topic that matches the desired destination. Topics for command messages to the teensy_interface:
- MQTT topic ricbot/cmd/T0 for the Teensy, the message is the string to send to the Teensy.
- MQTT topic ricbot/cmd/shutdown to schedule a shutdown of the RICBOT (power off), something like 20 seconds after the message.
- MQTT topic ricbot/cmd/ti for messages to the teensy_interface, the message is a string.
Install
The robot's interface is via MQTT. Install the MQTT ROS client
sudo apt install ros-jazzy-mqtt-client
Or directly as source
cd src git clone https://github.com/ika-rwth-aachen/mqtt_client
Compile:
cd ~/ros2_ws colcon build
Run MQTT_client
To start the mqtt_client:
cd ros2_ws/src/mqtt_client/mqtt_client/config ros2 launch mqtt_client standalone.launch.xml params_file:="params.teensy.yaml"
The parameter file should be extended with more mqtt2ros topics as needed.
This will launch the un-modified mqtt_client node with specific bridge parameters as specified in params.teensy.yaml:
/**/*:
ros__parameters:
broker:
host: localhost
port: 1883
tls:
enabled: false
client:
id: ros
clean_session: true
keep_alive_interval: 20.0
bridge:
ros2mqtt:
ros_topics:
- /teensy/cmd/T0
- /teensy/cmd/shutdown
- /teensy/cmd/ti
/teensy/cmd/T0:
mqtt_topic: ricbot/cmd/T0
primitive: true
inject_timestamp: false
/teensy/cmd/shutdown:
mqtt_topic: ricbot/cmd/shutdown
primitive: true
inject_timestamp: false
/teensy/cmd/ti:
mqtt_topic: ricbot/cmd/ti
primitive: true
inject_timestamp: false
mqtt2ros:
# Needs to be expanded to relevant topics
mqtt_topics:
- ricbot/data/T0/info
- ricbot/data/T0/hbt
ricbot/data/T0/info:
ros_topic: /teensy/T0/info
primitive: true
ricbot/data/T0/hbt:
ros_topic: /teensy/T0/hbt
primitive: true
Test interface
Start the teensy_interface with the right ini-file:
cd ~/svn/robobot/teensy_interface/build ./teensy_interface -z ricbot.ini
This should respond with something like:
$ ./teensy_interface -z ricbot.ini # UService:: created directory log_20260118_083120.745/ # UMqtt:: connection to MQTT broker on tcp://localhost:1883 established # UMqttIn:: connection to MQTT broker on tcp://localhost:1883 established # STeensy:: opening to USB /dev/ttyACM0 # SRobot:: (t0) found IP 0: eno1 192.168.2.157 # STeensy:: just connected # UService:: setup of Teensy 0 modules finished OK. # Type quit to stop, or 'h' for help
Start the mqtt_client in ROS
cd ros2_ws/src/mqtt_client/mqtt_client/config ros2 launch mqtt_client standalone.launch.xml params_file:="params.teensy.yaml"
There should now be hbt (heartbeat) message on the ROS side:
ros2 topic echo /teensy/T0/hbt
This should give something like:
data: '1768722645.7425 1738.4885 93 1748 4.85 0 9 18.1 0 0 ' --- data: '1768722646.2426 1738.9885 93 1748 4.85 0 9 18.0 0 0 ' --- data: '1768722646.7431 1739.4885 93 1748 4.85 0 9 18.0 0 0 ' ---
The data is: timestamp (host), timestamp Teensy, Teensy ID, version, battery voltage, ... (the rest depend on the platform).