Robobot teensy interface
Back to Robobot_B
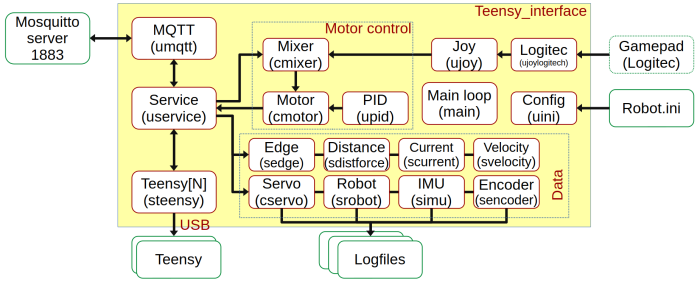
Teensy interface
The Teensy_interface app has the functions:
- Translate between the USB connection and the MQTT protocol.
- Adds motor velocity control (allow control using linear velocity and rotation velocity)
- Allow log of almost all relevant data to individual logfiles. Intended for debugging and import into Matlab.
- Monitors the IP addresses of the Raspberry and sends the result to the small Teensy display.
The app is configured with the file robot.ini
Teensy to MQTT
The teensy_interface app can interface with multiple Teensy boards, but for Robobot, only one Teensy board is available.
The Teensy data can be converted to an MQTT message directly, which is the default method.
The Teensy data message for raw line-sensor AD values has the format.:
liv 731 928 962 866 888 902 828 613 50
In MQTT, this will be split into a topic and a message.
topic: robobot/drive/T0/liv message: 1736776814.3819 731 928 962 866 888 902 828 613 50
The first part of the topic, robobot/drive/T0, is the same for all messages from the Teensy.
If you want to subscribe to all MQTT messages, the topic request could be robobot/drive/#.
The message is preceded by a timestamp indicating when the message was received from Teensy. The timestamp is seconds from the start of the epoch (1 Jan 1970), which is standard for all PCs
The MQTT block is duplicated. This is unnecessary, as all clients can receive and publish. A timing analysis showed that a receive introduced a 40- to 80-ms delay in publishing. The fix was to establish two clients: one for publication and one for receiving.
Data extract
The most relevant data is decoded in the interface and, in some cases, slightly reformatted before being sent to MQTT.
The decoded data can further be saved to individual logfiles.
Log files
Every time the app is started, typically when rebooted, a new log directory with the timestamp is created. This is the default behaviour.
cd ~/svn/robobot/teensy_interface/build ls CMakeCache.txt log_20250113_150013.267 Makefile CMakeFiles log_20250113_150828.688 out_console.txt cmake_install.cmake log_20250113_154849.030 out_err.txt log_20250113_111703.472 log_20250113_154849.170 robot.ini log_20250113_135545.064 log_20250113_154849.256 teensy_interface log_20250113_140824.729 log_20250116_171856.006
Here are the log file directories for 13 Jan and 16 Jan 2025.
Data logging is not started until the Python app is started with the line service.send("robobot/cmd/ti", "log 1"). Logging stops either immediately or after 15 minutes (set in the configuration file). This ensures the disk is not filled with log files when the robot is not on any mission.
The data usage can be relatively high; an example could be:
ls -l log_20250113_150013.267/ total 3288 -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 335 Jan 13 15:00 log_joy_drive.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 1371 Jan 13 15:00 log_joy_logitech.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 502 Jan 13 15:00 log_mixer.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 1447025 Jan 13 15:00 log_mqtt.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 416 Jan 13 15:07 log_service.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 76 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_acc_1.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 21885 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_dist.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 104242 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_edge_liv.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 58241 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_encoder.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 63071 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_encoder_velocity.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 78 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_gyro_1.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 3899 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_hbt.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 101085 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_motor_0_pid.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 99406 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_motor_1_pid.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 123413 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_motor_current.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 119760 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_motor_voltage.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 238992 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_pose.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 122 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_servo.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 923169 Jan 13 15:00 log_t0_teensy_io.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 local local 2474 Jan 13 15:00 robot.ini
The first line, total 3288, shows that the log files use 3288 kilobytes of disk space, and this is a 30-second recording. log_t0_teensy_io and log_mqtt hold all communication with the Teensy and MQTT. They are for debugging only and can be disabled in the robot.ini file.
Unused log files can be removed by:
cd ~/svn/robobot/teensy_interface/build rm -r log_20250113*
In this case, delete all 13 Jan 2025 log files.
Motor control
Motor control translated the drive command, linear velocity (m/s), and rotation speed (rad/s) into a motor voltage sent to the Teensy.
A drive command is typically sent from the Python app by MQTT topic robobot/cmd/ti, e.g. service.send("robobot/cmd/ti", "rc 0.25 0.5") for a linear velocity of 0.25m/s and a rotation speed of 0.5rad/s.
The mixer module calculates each wheel's needed velocity to satisfy the drive command.
The motor module uses closed-loop control to implement wheel velocity. The controller is a PID type. The parameters are configured in the robot.ini file. The measured velocity is taken from the velocity data module.
Gamepad control
There is an optional way to control the robot using a gamepad (Logitech is the only supported brand).
Manual control takes over when the back button on the gamepad is pressed.
Configuration file
All modules are configured by the settings in the robot.ini file. Especially:
- Data subscription from Teensy for essential data (like wheel velocity)
- data subscription is set by the entries like interval_vel_ms = 15 in the [encoder0] group for 15-ms interval for velocity updates.
- Wheel size and other static configuration data (like wheel radius)
- Wheel radius is set in the [mixer] group with wheel_radius = 0.077 for 77mm.
- Logfile settings (true or false)
The configuration is divided into groups. All Teensy data groups have an added 0 to indicate the first (and in this case only) Teensy board.
The configuration file is a text file, and a sample (SVN version 1235 (Jan 2026)) is:
[service] use_robot_hardware = true logpath = log_%d/ ; the '%d' will be replaced with date and timestamp (must end with a '/'). = max_logging_minutes = 60.0 log_service = true [mqtt] broker = tcp://localhost:1883 context = drive clientid = tif_data system = robobot/ function = drive/ print = false log = true use = true [mqttin] broker = tcp://localhost:1883 context = drive clientid = tif_cmd function = cmd/ system = robobot/ log = true print = false use = true [teensy0] use = true type = robobot idx = 105 ; robot 'name' and 'idx' are read-only, use command line option to change = name = Oliver device = /dev/ttyACM0 devicealt = /dev/ttyACM1 log = true print = false confirm_timeout = 0.04 encrev = true hardware = 8 [robot0] log = true print = false regbot_version = 1033 batteryusedwh = 106.892433 batterycalibrate = 1.0 robotnamepath = /home/local/svn/log/robotname [encoder0] interval_vel_ms = 8 interval_pose_ms = 5 log_enc = true log_pose = true print = false encoder_reversed = false [imu1teensy0] interval_gyro_ms = 12 interval_acc_ms = 12 gyro_offset = 0 0 0 log = true print_gyro = false print_acc = false [imu2teensy0] use = false [servotn0] interval_ms = 0 log = true print = true [velocity0] enctickperrev = 68 motorscale = 1 1 useteensyvel = true log = true print = false [motor_teensy_0] m1kp = 7.0 m1lead = 0 1.0 m1taui = 0.05 m1feedforward = 0 m1maxmotv = 10.0 m1voffset = 0.0 m2kp = 7.0 m2lead = 0 1.0 m2taui = 0.05 m2feedforward = 0 m2maxmotv = 10.0 m2voffset = 0.0 log_voltage = false m1log_pid = false m2log_pid = false m1print = false m2print = false interval_motv_ms = 33 interval_motpwm_ms = 0 relax_sec = 3.5 [current_teensy_0] log = false print = false interval_ms = 33 [distforce0] interval_ird_ms = 25 log_dist = true log_force = false print = false force = false [edge0] log = true print = false interval_liv_ms = 50 interval_livn_ms = 10 [gpio] # e.g. pins_out = "20=1 16=0" pins_out = stop_on_stop = true blink_period_ms = 600 log = true print = false # GPIO is used by Python script, not here use = false [mixer] use = true log = true print = false driveleft = 0 0 -1 driveright = 0 1 -1 wheelbase = 0.22 motor_gear = 19 drive_gear = 1 wheel_radius = 0.075 [joy_logitech] log = true print = false device = /dev/input/js0 [joy_use] log = true print = false drive_control = true vel_limit = 0.8 vel_axis = 4 turn_limit = 10.0 turn_axis = 3 button_fast = 5 slow_factor = 0.3 axis_servo = 1 servo = 1 servoscale = 10 [ini] ; set 'saveconfig' to 'false' to avoid autosave = saveconfig = true version = 1215 2026-01-18 11:15:45
Command line options
The teensy_interface has a few command-line options, including help. The command line help is:
cd ~/svn/robobot/teensy_interface/build ./teensy_interface -h ROBOBOT app Usage: ./teensy_interface [OPTIONS] Options: -h,--help Print this help message and exit -v,--version Compiled SVN version (for uservice.cpp) -d,--daemon Do not listen to the keyboard (daemon mode) -l,--logging-off Do not start logging right away (wait for MQTT log message) -g,--gyro Calibrate gyro offset -t,--time FLOAT Open all sensors for some time (seconds) -n,--number INT Set name number to Teensy part [0..150] use with --interface. -i,--interface INT Set interface number to Teensy 0..0 (default is 0) -H,--hardware INT Set robot hardware type (most likely 8) use with --interface. -z,--initialization TEXT Specify which initialisation file to use, default is robot.ini
When the app is started at boot time, the options "-d -l" are used to not start logging and not listen to the keyboard.