Fejemis Teensy
Back to fejemis
Drive Teensy
This unit calculates the odometry pose and controls the driving wheels.
Meta info
The default messages from the USB connection is the hbt (heartbeat), like:
hbt 44.97199 90 110 24.95 10 0 hbt 45.37199 90 110 24.95 10 0 hbt 45.77198 90 110 24.95 10 0 hbt 46.17198 90 110 24.95 10 0 hbt 46.57199 90 110 24.96 10 0 hbt 46.97199 90 110 24.91 10 0
The first parameter is Teensy time (seconds); the next is the ID (drive is 90, front is 91); the next is the version (here 110) and battery voltage, here 24.9V.
Steer position from front processor
The command needs to know the steering wheel angle. The steering angle is provided from the front processor by the command (every 15ms):
sub fwl 15
The result is like this (one line every 15ms)
fwl 10.50 0x0 0x3c2 fwl 10.37 0x0 0x3c2 fwl 10.06 0x0 0x13c2 fwl 8.44 0x0 0x13c2 fwl 7.56 0x0 0x3c2 fwl 5.52 0x0 0x3c2 fwl 4.24 0x0 0x13c2 fwl 1.58 0x0 0x13c2 fwl 0.29 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -1.80 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -2.61 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -3.71 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -4.00 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -4.42 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -4.53 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -4.66 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -4.75 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -4.92 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -5.05 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -5.45 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -5.69 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -6.11 0x0 0x3c2 fwl -6.37 0x0 0x13c2 fwl -6.79 0x0 0x13c2
The first value is the steering wheel angle in degrees (positive is left), the next value is error flags (should be zero). The third value is diagnosis (should end with '3C2'):
Bit 11:12 SPI frame counter Bit 10 Error flag broken Hall element (should be 0) Bit 9 Initial AGC settling finished (should be 1) Bit 8 Error flag offset compensation finished (should be 1) Bit 7 Sine offset compensation finished (should be 1) Bit 6 Cosine offset compensation finished (should be 1) Bit 5 Error flag magnitude is below half of target value (should be 0) Bit 4 Warning flag AGC high (should be 0) Bit 3 Warning flag AGC low (should be 0) Bit 2 Error flag CORDIC overflow (should be 0) Bit 1 All magneto core loops finished (should be 1) Bit 0 VDD supply mode: 0: 3V; 1: 5V (should be 0 for 3.3V supply)
Drive command
Both the drive processor and the front processor should be given the same command, like:
rc 1 0.5 65
The first value 1 is intended as the command source for priority (from 1 to 10, where 1 is highest priority), this is not (pt) implemented. The second value 0.5 is the desired velocity in m/s (forward is positive). The third value 65 is the desired turn rate in degrees/s (positive is left turn).
USB Interface
The following list shows the result of sending the fejemis_drive a 'help' command (taken from the GUI when connected to the USB directly):
------ Commands available for drive ------- veri and 'sub ver N' get version number and version string (and 'sub ver N') leave Stop all subscribed data - stop sending data help This help text. Sensor ------- adci and 'sub adc N' Get raw ADC values (12V, current, IR1, IR2, motorV) inti and 'sub int N' Get number of interrupts for ADC1 and ADC2 bati and 'sub bat N' Get battery voltage and current (volt [V], amp [A], lipo cells [N] timei and 'sub time N' Get timing info (cycle time[us], sense [us], +control[us], +logetc [us], adc cycle [us], adc cycles/control) ampi and 'sub amp N' Get current [A], ad4, ad5, adFactor, offset0, offset1 Logger help ----------- log XXX m Start control log every m ms (XXX = pose, time, usb, vel) log pose m Start pose control log every m ms (>= 1 ms) log get Get log (has=0/10 entries) log usb log USB io log stop Stop current log (no effect if log is full already) Drive control ------ rc e v t Set control reference e=1:gamepad, e=2:run, v=velocity (m/s), t=turnrate degree/sec fwl a Tell current front wheel angle (in degrees, 0 is forward, left is positive) confs B F Set steering configuration (B=wheelbase, F=dist to steering wheel [m]) cvdrivei and 'sub cvdrive N' Get current control values cpdrivei and 'sub cpdrive N' Get control parameters. N = use,Kp,useI,taui,ilimit,1,useLeadf,tz,tp,useLeadb,tz,tp,usePre,tz,tp,useULim Ulim confsi and 'sub confs N' Get robot steer config 'confs steer-base wheel-bae' (meters) State settings ------- setid N Set device ID to N (id=90, part of hbt) id=0 for factory settigs. setname string Set device name to string (< 32 chars) should be 'drive'. stop Stop. No control allowed until a start is received start Allow control (default) rcSource=10 (-1=stopped) off T Turn off power (cuts power after T seconds) on Power on (works only if not on battery) hbti and 'sub hbt N' Get time and state (heartbeat) idi and 'sub id N' Get device name and number IMU help ------- gyroc Start gyro calibration (finished=1) magcal Set magnetometer calibration values (offset[3] rotate/scale[9]) acccal Set accelerometer calibration values (offset[3] scale[3]) acccal2 make simple acceleration calibration with horizontal board gyroi and 'sub gyro N' Get current gyro value as 'gyro gx gy gz' (deg/s) gyrooi and 'sub gyroo N' Get gyro offset 'gyroo ox oy oz' acci and 'sub acc N' Get accelerometer values 'acc ax ay az' (m/s^2) accoi and 'sub acco N' Get accelerometer offset values 'acco xo yo zo' (m/s^2) magi and 'sub mag N' Get magnetometer values 'mag mx my mz' (uT) magwi and 'sub magw N' Get magnetometer raw values 'magw mx my mz' (uT) magoi and 'sub mago N' Get magnetometer offset values 'mago xo yo zo r11 r12 r13 r21 ... r33' (uT) imuposei and 'sub imupose N' Get IMU-based pose 'imupose roll pitch yaw (radians) Encoder help ------- enc0 Reset pose to (0,0,0) confw rl rr g t wb Set configuration (radius [m] gear [>=1] encTick [n/rev] wheelbase [m]) enci and 'sub enc N' Get encoder value 'enc encoder interrupts' (integer) posei and 'sub pose N' Get current pose 'pose t x y h' (sec,m,m,rad) veli and 'sub vel N' Get velocity 'left right' (m/s) confi and 'sub conf N' Get robot conf (radius, radius, gear, pulsPerRev, wheelbase, sample-time) TOF distance help ------- tofdi and 'sub tofd N' Get distance in meters from time of flight (TOF) sensor tof1i and 'sub tof1 N' Make TOF distance measurement HC-SR04 distance help ------- hcsr Trigger new measurement sr04i and 'sub sr04 N' Get distance in meters from HC-SR04 sensor EE (configuration flash) -------- eew save configuration to EE-Prom (flash) eer Read configuration from EE-Prom
Each section relates to a software module.
Turning control
The turning in the drive unit receives two messages:
- Linear velocity desired (v in m/sec) and turnrate w in radians/sec (RC message)
- Angle of front-wheel (in degrees) (from fwl message)
The angle of the front wheel is used to calculate a turning radius d (for the other wheel).
d = f/tan(theta) + B/2
where f is the distance to the steering wheel, theta is the angle of the front wheel and B is the drive base, the distance between the driving wheels.
The turn radius d is from the turning centre to the other wheel (the fastest wheel). This wheel should have the desired velocity v2. The outer wheel velocity should not be zero. When the desired velocity v is zero, the speed of the outer wheel is therefore combined with the turn rate w as:
v2 = sqrt(v^2 + w^2)
With the sign from the linear velocity v. w is here assumed to be in radians, and with the robot's wheelbase (B = 0.4m), it seems OK.
The inner wheel should then have a velocity v1 dependent on the turn radius d, the wheelbase and the velocity of the other wheel v2
v1 = v2 - v2 * B / d
The sign of theta determines which wheel should have the higher velocity.
Front Teensy
The front Teensy controls the steering angle of the front wheel.
Meta info
The default messages from the USB connection is the hbt (heartbeat), like:
hbt 34.7925 91 100 0.00 1 0.011 hbt 35.1923 91 100 0.00 1 0.011 hbt 35.5921 91 100 0.00 1 0.009 hbt 35.9918 91 100 0.00 1 0.009 hbt 36.3916 91 100 0.00 1 0.009
The first parameter is Teensy time (seconds); the next is the ID (drive is 90, front is 91), followed by the version number (100); see the source code for the rest.
Steering command
The steering command is the same as for the drive processor:
rc 1 0.5 65
The first value 1 is intended as the command source for priority (from 1 to 10, where 1 is highest priority), this is not (pt) implemented. The second value 0.5 is the desired velocity in m/s (forward is positive). The third value 65 is the desired turn rate in degrees/s (positive is left turn).
Conversion to angle
The desired front wheel angle is then
- angle = atan2(S * w, v);
Where w is the turn rate in radians/s, v is the desired velocity in m/s and S is the distance to the steering wheel.
The steering angle is then converted back to degrees/s as control reference.
Steer controller
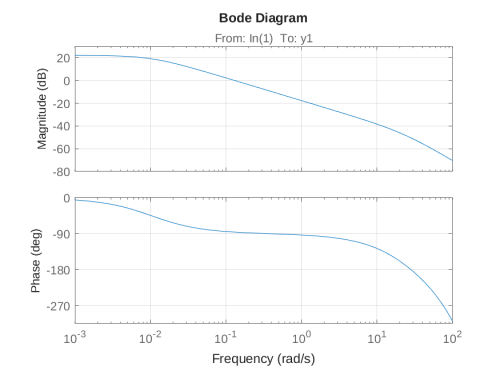
MATLAB estimates the steer controller transfer function with an added ZOH approximation of 25 ms. This estimate fits reasonably with how fast the servo (a HerculeX DRS0101) can handle commands.
The resulting Bodeplot is:
Where input is velocity control value for the Herculex in range -1000..1000 and output is steering angle in degrees.
A P-Lead controller is designed with a phase margin of 80 degrees and a Lead aplha=0.3 to give
- Crossover frequency 12 radians/s
- Kp = 43
- tau_d = 0.16 s
Actual steering angle
The actual steering angle should be used by the drive system. This angle subscribed by the command every 15 ms by:
sub fwl 15
See the drive command above for more details.
Lift brush system
A linear actuator controls the height of the steering wheel.
The command that controls the motor is, e.g.:
motv 6 4
Where 6 is the motor voltage (-12..12V), a positive value lifts the wheel. The second parameter 4 is the time in seconds for the motor voltage.
It takes about 12 seconds from end to end at 6V actuator voltage.
The lead (brush battery) voltage sensing is not implemented.
USB interface
The allowed commands to the front Teensy are:
help This help text.
------ State settings -------
setid N Set device index to N (id=91, part of hbt).
setname string Set device name to string (< 32 chars) should be 'front'.
brush 0/1 Turn on/off for power to the brush
hbti and 'sub hbt N' Get time and state (heartbeat)
idi and 'sub id N' Get device ID (name and number)
----- LED control -----
led N R G B Set led number N (0..11) to this RGB value (0..255).
ledb R G B Set band color RGB value (0..255).
leds Set to default values
ledon V Turn LED strip op V=1 or off V=0
---- EE (configuration flash) --------
eew save configuration to EE-Prom (flash)
eer Read configuration from EE-Prom
------ Motor help -------
motv m1 time Set motor voltage -12.0..12.0 for this time (in seconds)
pwmf F Set PWM frequency (is=15000)
moti and 'sub mot N' Get motor voltage 'mot m1(V) 0 0 0 0 PWM-frq(Hz)'
------ Encoder help -------
enc0 Reset position and encoder to 0
------ Sensor -------
adci and 'sub adc N' Get raw ADC values (12V, current, IR1, IR2, motorV)
inti and 'sub int N' Get number of interrupts for ADC1 and ADC2
bati and 'sub bat N' Get battery voltage and current (volt [V], amp [A], lipo cells [N]
timei and 'sub time N' Get timing info (cycle time[us], sense [us], +control[us], +logetc [us], adc cycle [us], adc cycles/control)
curi and 'sub cur N' Get current [A], ad4, ad5, adFactor, offset0, offset1
------ IR distance -------
irc A1 B1 A2 B2 Set calibration values A=13cm, B=50cm (sensor 1 and 2)
iri and 'sub ir N' Get IR and calibration data 'irc dist1 dist2 ... (meter)
------ Steering servo -------
svp P T Set servo position (P=0..1000, time T 0..254).
svv V T Set servo velocity (V=0..1000, acc-time T= 0..254).
svat T Set acceleration time (T=0 rectangle, M>0 is M*11.2ms) - no effect in vel mode?.
svar R Set acceleration ratio (R=0 fast, R>slower) - no effect in vel mode?.
svjt T Set servo jog time (T=0..255 x 11.2ms)
svb B Set servo communication Baud rate (default=115200)
svscan Id Scan for servos on serial bus from Id = 0..254.
svpi and 'sub svp N' Get current servo position
svjti and 'sub svjt N' Get jog time, accRatio, accMax time ('svjt jog ratio max')
------ Front wheel position -------
pds Print debug string from AS driver.
read V Read angle or not (debug).
fwoffset A I Set front wheel offset (deg), I=1 invert angle.
fwli and 'sub fwl N' Get current front wheel angle 'fwl ang(deg) err disg'
fwoi and 'sub fwo N' Get front wheel offset 'fwo ofset reverse'
------ Steering control -------
rc S v w Drive command: S is source 1..10, v: velocity m/s, w: turnrate degrees/s (positive is left)
cssteer E ... Set front angle controller (see ucontrolbase.cpp for params).
confs B S Set wheel base and steer base (in meters)
cvsteeri and 'sub cvsteer N' Get current control values
cpsteeri and 'sub cpsteer N' Get control parameters
confsi and 'sub confs N' Get robot steer config 'confs steer-base wheel-bae' (meters)
Each section relates to a software module.
Turning control
The front wheel receives the movement command (RC) with
- desired linear velocity v
- desired turn rate w
The associated turn angle theta of the front wheel can then be calculated as
theta = atan2(f * w, v)
where f is the distance to the front wheel, w is the desired turn rate, B is the wheelbase between the driving wheels and v is the desired linear velocity.
The angle is presented to a servo control loop and the actual steering angle is measured and send to the drive Teensy (through the bridge).
The theta angle is allowed in the range of -90 deg to +90 deg.
Teensy Software structure
Figure: The Teensy software is structured with a main loop and a number of units. After reset all units are initialized in a setup function, after that the main loop is entered. The main loop services the USB and send commands to the units for decoding. At regular intervals, the sample clock tick, all units are called to execute any sample time function. Most units are interfaces to external devices such as IMU, motor drive or distance sensor. There is further support units for e.g. control.
Setup - loop overview
The setup and loop structure follows the Arduino sketch format. The file is a C++ file as the compilation is using a Makefile rather then the Arduino IDE.
The main file (main.cpp) code has this structure (shortened for clarity)
void setup() // INITIALIZATION
{
usb.setup();
led.setup();
imu.setup();
enc.setup();
sensor.setup();
motor.setup();
state.setup();
}
void loop(void)
{
usb.send("# Starting main loop\n");
while ( true )
{ // main loop
usb.tick(); // incoming command service
if ( startNewCycle ) // start of new control cycle
{ // mostly every 1ms
imu.tick(); // for heading estimate
sensor.tick(); // AD converter, e.g. battery maintenance
irdist.tick(); // distance sensor
enc.tick(); // wheel encoder and odometry
state.tick(); // e.g. emergency stop
control.tick(); // feedback control
motor.tick(); // motor control
}
}
}
Unit structure
Figure: Each unit is coded in a separate file and has about the same structure. The unit is a class that holds the data from or to the device. The device is configured when the setup is called. The data from the device, or calculated from the data, is made available for subscription using a subscription class called USubss. The device is accessed using a standard Arduino-type library, for e.g. a I2C or an A/D interface. The unit may have configuration that need to be saved, e.g. calibration data or device mode that can be set from the interface, but needs to be saved.
Command decode
Commands from the USB connection is line oriented and consist of one line of text starting with a keyword. The line ends with a "new-line" (\n) or a combination if "carriage-return" (\r) and "new-line".
Request of data can be just the keyword, e.g.:
help (for on-line help - list of available commands) gyroi (for one-time information about gyro measurement) bati (for one-time info about battery voltage)
or a keyword with parameters
ctrli vel (to get all the PID control parameters for velocity control)
Issue commands or send data, e.g.:
motv m1 m2 (to set motor 1 (left) and motor 2 (right) to a specified voltage. rc e v t (to do remote drive control with velocity "v" and turn-rate "t") "e" should be 2 for non-manual control.
Subscription
From the USB most data can be subscribed with the a line starting with the keyword "sub", e.g.:
sub gyro 10 (for subscription to gyro data every 10ms) sub bat 200 (for subscription to battery status every 200ms)
The available subscriptions are generated in the "setup" part of the unit and holds also the on-line help text.
E.g. the wheel encoder unit has this subscription setup code (in enc.cpp):
void setup()
{
...
addPublistItem("enc", "Get encoder value 'enc encoder interrupts' (integer)");
addPublistItem("pose", "Get current pose 'pose t x y h' (sec,m,m,rad)");
addPublistItem("vel", "Get velocity 'left right' (m/s)");
addPublistItem("conf", "Get robot configuration (radius, radius, gear, pulsPerRev, wheelbase, sample-time)");
}
At tick-time subscriptions are serviced, and if it is time, the "sendData(item)" is called, e.g. for the wheel encoder unit:
void UEncoder::sendData(int item)
{
if (item == 0)
sendEncStatus();
else if (item == 1)
sendPose();
else if (item == 2)
sendVelocity();
else if (item == 3)
sendRobotConfig();
}
Configuration save
The Teensy has 4096 bytes of configuration flash memory, this is used to store settings and calibration values.
The use of this memory is controlled by the "config save" unit in the file "eeconfig.cpp".
The unit is controlled by two commands "eew" (save) and "eer" (load). On reset the configuration is loaded.
If the ID number is set to "0", all configurations are reset (to factory settings). To save any configuration, set ID number with the command "setid N" where N is a number > 0.
Configuration is saved as a stack, and each unit must therefore save and load exactly the same amount of data. Add load and save to the list in "eeconfig.cpp" when new units are added that need configuration saved.
The load and save are like e.g.:
void UImu::eePromSave()
{
eeConfig.push32(offsetGyro[0]);
eeConfig.push32(offsetGyro[1]);
eeConfig.push32(offsetGyro[2]);
// accelerometer
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
eeConfig.pushFloat(accOffset[i]);
}
void UImu::eePromLoad()
{
offsetGyro[0] = eeConfig.read32();
offsetGyro[1] = eeConfig.read32();
offsetGyro[2] = eeConfig.read32();
gyroOffsetDone = true;
//
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
accOffset[i] = eeConfig.readFloat();
}
Update tick
The timing is based on a 10 us timer and the following is defined (in "main.cpp")
// control period is time between control calls // and is in units of 10us, ie 125 is 1.25ms or 800Hz #define CONTROL_PERIOD_10us 100 // sample time in seconds #define SAMPLETIME (0.00001 * CONTROL_PERIOD_10us)
The SAMPLETIME is a floating point number in seconds. The example above is for 1ms sample time.
All units tick() function is called at this interval. For new units the call must be added in the main code, like for the motor unit:
void UMotor::tick()
{ //
implementMotorVoltage();
// subscription
subscribeTick();
}
It there is data subscription associated with this unit, then the subscribeTick() must be called to service the subscriptions.