Robobot software description: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Back to [[ | Back to [[Robobot B | Robobot]] | ||
== C++ development == | |||
=== C++ main structure === | |||
<!-- [[File:c++main.png | 220px]] --> | |||
Introduction to the main source code structure. | |||
[[C++ main entry point]] | |||
=== Compile and CMake === | |||
<!-- [[Robobot compile]] --> | |||
== Functional description == | == Functional description == | ||
=== Software class - and | === Software class - and example === | ||
<!-- [[File:class-def20.png | 200px]] --> | |||
This page also has an explained behaviour plan example (bplan20). | |||
[[Robobot software building blocks | C++ building blocks]] overview. | [[Robobot software building blocks | C++ building blocks]] overview. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 27: | ||
=== Low-level robot control === | === Low-level robot control === | ||
[[File:robobot_level_1.png | 300px]] | <!-- [[File:robobot_level_1.png | 300px]] --> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 36: | ||
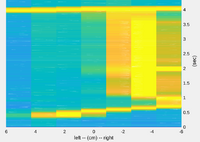
[[File:line-sensor-1_heatmap.png | 200px]] | [[File:line-sensor-1_heatmap.png | 200px]] | ||
[[Robobot linesensor description | Line sensor]] | Description of the [[Robobot linesensor description | Line sensor]] functionality. | ||
== Robot.ini configuration file == | |||
[pose] | |||
gear = 19.0 | |||
wheeldiameter = 0.146 | |||
enctickperrev = 64 | |||
wheelbase = 0.243 | |||
log = true | |||
print = false | |||
See [[Raubase configuration file]] for explanation. | |||
== Make a new behaviour plan == | |||
The easy way to make a new behaviour plan module is to copy an existing plan and rename a number of elements. | |||
See [[Robobot_new_behaviour_plan]]. | |||
== Sensor calibration == | |||
See [[Robobot sensor calibration | sensor calibration]], which covers odometry, distance sensor, and gyro. | |||
Calibration of the [[Robobot linesensor description | line sensor is found here]]. | |||
[[Camera calibration]] is needed, as the lens distorts the image quite a bit. | |||
== Video streamer == | |||
A video streamer called 'motion' is installed. | |||
The motion config file need a few changes: | |||
sudo nano /etc/motion/motion.conf | |||
Set in the 'System control' group | |||
* log_file /home/local/.motion/motion.log | |||
* target_dir /home/local/Videos/motion | |||
* video_device /home/local/video0 (or as needed) | |||
In the 'Live stream' group | |||
* stream_localhost off | |||
=== run motion === | |||
To run the streamer, SSH to the robot and start motion | |||
$ motion | |||
[0:motion] [NTC] [ALL] conf_load: Processing thread 0 - config file /etc/motion/motion.conf | |||
[0:motion] [NTC] [ALL] motion_startup: Logging to file (/home/local/.motion/motion.log) | |||
NB! Remember to stop the streamer before trying to use the camera for other purposes. | |||
Stop by ctrl-C | |||
=== View the stream === | |||
To view the result, use a browser to open the address of the robot and port 8081, e.g. if the robot has IP '192.168.1.151': | |||
192.168.2.151:8081 | |||
You should now see a stream of default 640x480 at 10 FPS as default; more options are available in /etc/motion/motion.conf. | |||
The stream has a significant delay, and the framerate may be lower if the network is slow. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:05, 28 April 2024
Back to Robobot
C++ development
C++ main structure
Introduction to the main source code structure.
Compile and CMake
Functional description
Software class - and example
This page also has an explained behaviour plan example (bplan20).
C++ building blocks overview.
Low-level robot control
Robobot level 1 with interface to hardware and pose generation.
Line sensor
Description of the Line sensor functionality.
Robot.ini configuration file
[pose] gear = 19.0 wheeldiameter = 0.146 enctickperrev = 64 wheelbase = 0.243 log = true print = false
See Raubase configuration file for explanation.
Make a new behaviour plan
The easy way to make a new behaviour plan module is to copy an existing plan and rename a number of elements.
See Robobot_new_behaviour_plan.
Sensor calibration
See sensor calibration, which covers odometry, distance sensor, and gyro.
Calibration of the line sensor is found here.
Camera calibration is needed, as the lens distorts the image quite a bit.
Video streamer
A video streamer called 'motion' is installed.
The motion config file need a few changes:
sudo nano /etc/motion/motion.conf
Set in the 'System control' group
- log_file /home/local/.motion/motion.log
- target_dir /home/local/Videos/motion
- video_device /home/local/video0 (or as needed)
In the 'Live stream' group
- stream_localhost off
run motion
To run the streamer, SSH to the robot and start motion
$ motion [0:motion] [NTC] [ALL] conf_load: Processing thread 0 - config file /etc/motion/motion.conf [0:motion] [NTC] [ALL] motion_startup: Logging to file (/home/local/.motion/motion.log)
NB! Remember to stop the streamer before trying to use the camera for other purposes.
Stop by ctrl-C
View the stream
To view the result, use a browser to open the address of the robot and port 8081, e.g. if the robot has IP '192.168.1.151':
192.168.2.151:8081
You should now see a stream of default 640x480 at 10 FPS as default; more options are available in /etc/motion/motion.conf.
The stream has a significant delay, and the framerate may be lower if the network is slow.