Robobot circuits: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
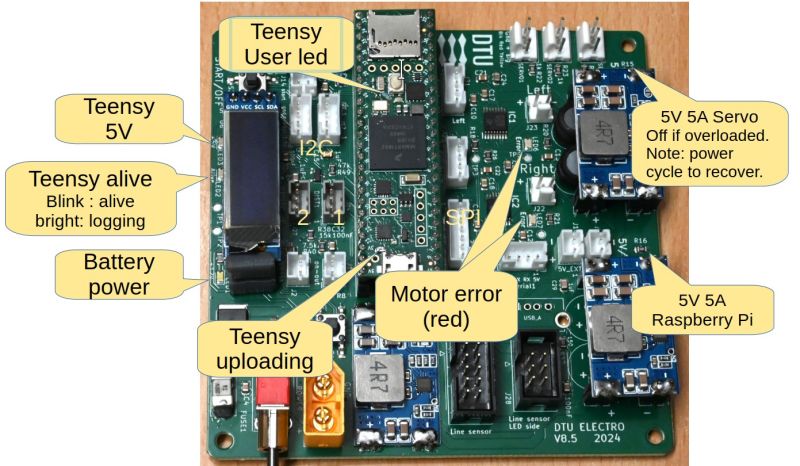
Figure 6. Connectors. Unused connectors are: 2 I2C plugs (I2C and I2C1), SPI plug (with driver for AS5147), ON-OUT that can be used to power on other similar boards (connect to on-in). | Figure 6. Connectors. Unused connectors are: 2 I2C plugs (I2C and I2C1), SPI plug (with driver for AS5147), ON-OUT that can be used to power on other similar boards (connect to on-in). | ||
=== PCB LEDs === | |||
[[file:PCB-leds-annotated.jpg | 800px]] | |||
== Line sensor == | == Line sensor == | ||
Revision as of 10:04, 2 February 2025
Back to Robobot_B
Digital IO
Circuit diagram
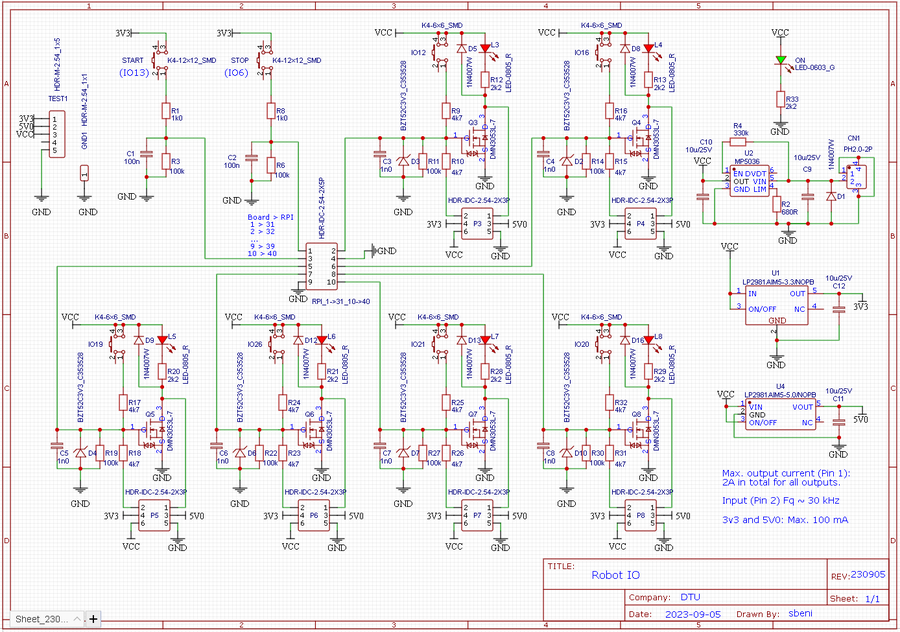
Figure 1. The circuit diagram should ensure that each IO pin can function as both input and output. If input, then the pin has active pull down, i.e. for input to change, it must be pulled high, to at least 3.3V, but 5 or 12V will work too. If output, then a transistor is active when output is high, and can draw at least 1A from the 12V supply. The 5V and 3.3V can supply no more than 100mA.
PCB
Figure 2. The PCB layout for the digital IO circuit.
Robobot
Circuit diagram
Figure 3. The Robobot circuit for version 8.5 (circuit is the same as version 8.4).
PCB
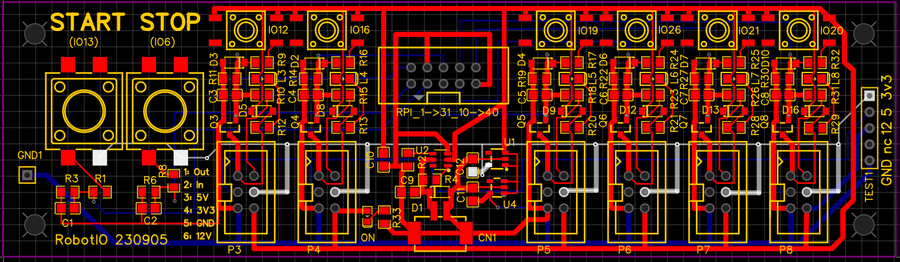
Figure 4. PCB with more trace details.
PCB view
Figure 5. Populated PCB with Teensy 4.1 and O-LED display.
PCB view annotated
Figure 6. Connectors. Unused connectors are: 2 I2C plugs (I2C and I2C1), SPI plug (with driver for AS5147), ON-OUT that can be used to power on other similar boards (connect to on-in).
PCB LEDs
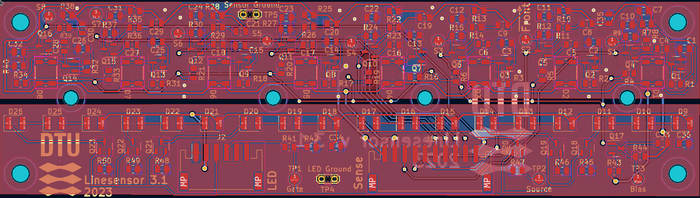
Line sensor
Circuit
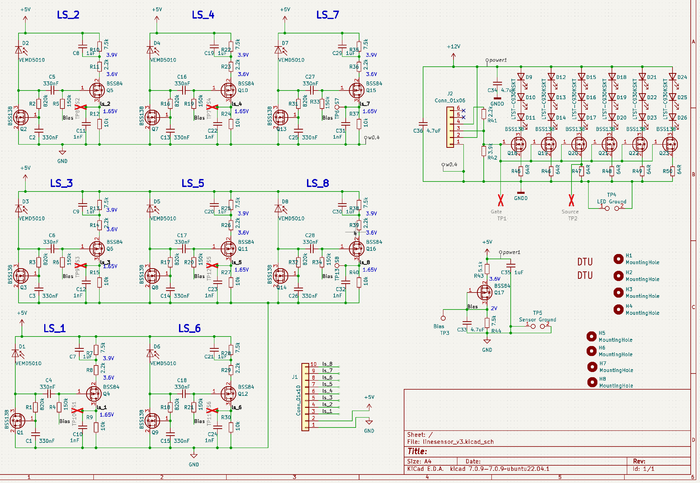
Figure 7. Circuit diagram for the line sensor. 8 sensors with a change amplifier and analogue output. The 18 LEDs provide the blinking light at the sample rate (on Regbot 1kHz).
PCB
Figure 8. The PCB in 3D view. The distance from the first to the last sensor is 12cm.
Figure 9. PCB layout.
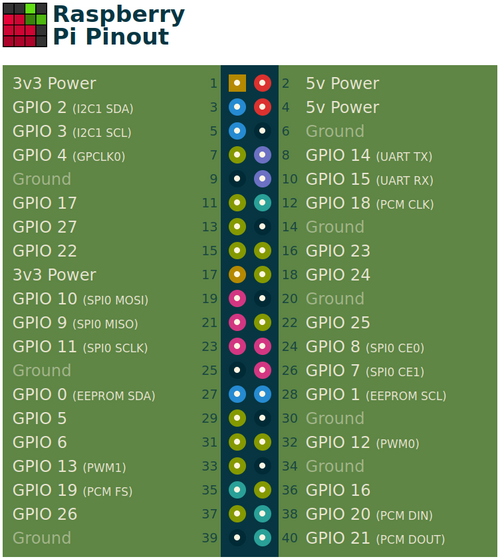
Raspberry PI
Figure 9. GPIO pin numbers, the bottom 10 pins are used for the IO-board. Pin1 on the cable match Pi pin 31 (GPIO6).