Robobot calibration: Difference between revisions
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Place the sensor at the expected distance over a white surface with the expected reflectance (i.e. white tape). | Place the sensor at the expected distance over a white surface with the expected reflectance (i.e. white tape). | ||
Send the command, e.g. | Send the command, e.g. ''licw 100'': | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | |||
message: "licw 100" | |||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | |||
message: "100" | |||
where 100 means average over 100 samples. | where 100 means average over 100 samples. | ||
Once finished, save the values in the Teensy flash by | Once finished, save the values in the Teensy flash by ''eew'': | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | |||
message "eew" | |||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | |||
message "" | |||
=== Get normalized data === | === Get normalized data === | ||
Subscribe to data from the Teensy | Subscribe to data from the Teensy using the command | ||
sub livn 7 | sub livn 7 | ||
Or using MQTT, publish: | Or using MQTT, publish: | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | ||
message: "livn 7" | message: "sub livn 7" | ||
where 7 means update every 7 ms. This could be as low as 1, but the traffic load may give communication bottlenecks resulting in delay or lost messages. The communication limit is approximately 4000 messages per second (each below 64 characters). | where 7 means update every 7 ms. This could be as low as 1, but the traffic load may give communication bottlenecks, resulting in delay or lost messages. The communication limit is approximately 4000 messages per second (each below 64 characters). | ||
== Distance sensor calibration == | == Distance sensor calibration == | ||
| Line 68: | Line 64: | ||
sub ir 300 | sub ir 300 | ||
Using MQTT this is: | Using MQTT this is: | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | ||
message: ir 300 | message: sub ir 300 | ||
Watch the message (either using cat or MQTT) | Watch the message (either using cat or MQTT) | ||
| Line 85: | Line 81: | ||
robobot/drive/T0/ir 1740853406.3075 0.124 0.137 15666 14207 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 | robobot/drive/T0/ir 1740853406.3075 0.124 0.137 15666 14207 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 | ||
Obstacles are here at 13 cm for both sensors. The first two values show the distance, | Obstacles are here at 13 cm for both sensors. The first two values show the distance, which is close to 13 cm here. The raw (filtered) values are approximately 15660 and 14210, respectively. This is relatively close to the already-calibrated value of 15000. | ||
The last value ''1'' shows that the sensor is on | The last value ''1'' shows that the sensor is on; if not, then send the on command: | ||
iron 1 | iron 1 | ||
Using MQTT | Using MQTT | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | ||
message: 1 | message: iron 1 | ||
==== Sensor values 50 cm ==== | ==== Sensor values 50 cm ==== | ||
| Line 115: | Line 111: | ||
irc 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 | irc 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 | ||
or MQTT, publish: | or MQTT, publish: | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | ||
message: "15660 4600 14210 4760 1" | message: "irc 15660 4600 14210 4760 1" | ||
Then save to the Teensy flash: | Then save to the Teensy flash: | ||
eew | eew | ||
or using MQTT | or using MQTT | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | ||
message "" | message "eew" | ||
The values at 50cm now look like: | The values at 50cm now look like: | ||
| Line 167: | Line 163: | ||
confw 0.0750 0.0750 19 92 0.234 | confw 0.0750 0.0750 19 92 0.234 | ||
or using MQTT | or using MQTT | ||
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | topic: robobot/cmd/T0 | ||
message: "0.0750 0.0750 19 92 0.234" | message: "confw 0.0750 0.0750 19 92 0.234" | ||
The values can be queried with a ''configi'' command, | The values can be queried with a ''configi'' command, which returns, e.g.: | ||
conf 0.0750 0.0750 19.000 92 0.2340 0.0020 0 | conf 0.0750 0.0750 19.000 92 0.2340 0.0020 0 | ||
or, if subscribed from MQTT | or, if subscribed from MQTT | ||
topic: robobot/drive/T0 | topic: robobot/drive/T0 | ||
message: 0.0750 0.0750 19.000 92 0.2340 0.0020 0 | message: conf 0.0750 0.0750 19.000 92 0.2340 0.0020 0 | ||
The last ''0.0020'' is the system sample time, here 2ms. The last ''0'' is for motortest only. | The last ''0.0020'' is the system sample time, here 2ms. The last ''0'' is for motortest only. | ||
The simple method is: | The simple method is: | ||
* Order the robot to drive 1m, check how long the robot | * Order the robot to drive 1m, check how long the robot thinks it has driven, e.g. 1.02m, then compare with reality, and adjust the wheel radius as relevant. | ||
* Order the robot to turn e.g. 180 degrees, compare with reality and adjust the distance between driving wheels as needed. | * Order the robot to turn, e.g. 180 degrees, compare with reality and adjust the distance between driving wheels as needed. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:42, 20 January 2026
Back to Robobot
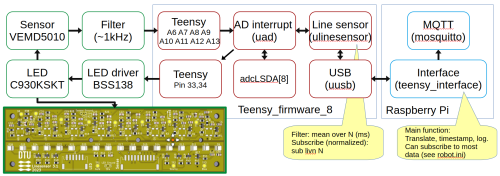
Sending commands to the Teensy board using MQTT
Line sensor
The line sensor blinks the LED illumination and subtracts the non-illuminated from the illuminated.
These (raw) values are then normalized relative to a calibrated expected white value.
The normalized value is between 0 (black - no reflection) and 1000 (calibrated white reflection).
Start calibration
Place the sensor at the expected distance over a white surface with the expected reflectance (i.e. white tape).
Send the command, e.g. licw 100:
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message: "licw 100"
where 100 means average over 100 samples.
Once finished, save the values in the Teensy flash by eew:
topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message "eew"
Get normalized data
Subscribe to data from the Teensy using the command
sub livn 7 Or using MQTT, publish: topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message: "sub livn 7"
where 7 means update every 7 ms. This could be as low as 1, but the traffic load may give communication bottlenecks, resulting in delay or lost messages. The communication limit is approximately 4000 messages per second (each below 64 characters).
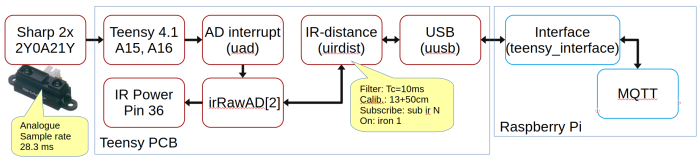
Distance sensor calibration
The distance sensor needs calibration.
The sensor is calibrated with two sensor values, 13 cm and 50 cm.
The datasheet states that the analogue voltage out of the sensor is something like:
It can be seen that distances below 5cm can give the same voltage as most other distances.
The easiest way is to have console access directly to the Teensy. Connect to the robot using, e.g., Putty to get two command lines on the Robot's Raspberry. Or a serial console if the Teensy is connected directly to a PC.
Sensor values 13 cm
Subscribe to sensor data and calibration values every 300ms:
Send this message to the Teensy
sub ir 300 Using MQTT this is: topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message: sub ir 300
Watch the message (either using cat or MQTT)
cat /dev/ttyACM0 Using MQTT, subscribe to topic: robobot/drive/T0/ir
Should get this
ir 0.124 0.137 15698 14219 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.124 0.137 15660 14220 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.124 0.137 15666 14207 15000 4600 15000 4100 1
or using MQTT
robobot/drive/T0/ir 1740853405.7074 0.124 0.137 15698 14219 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 robobot/drive/T0/ir 1740853406.0078 0.124 0.137 15660 14220 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 robobot/drive/T0/ir 1740853406.3075 0.124 0.137 15666 14207 15000 4600 15000 4100 1
Obstacles are here at 13 cm for both sensors. The first two values show the distance, which is close to 13 cm here. The raw (filtered) values are approximately 15660 and 14210, respectively. This is relatively close to the already-calibrated value of 15000.
The last value 1 shows that the sensor is on; if not, then send the on command:
iron 1 Using MQTT topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message: iron 1
Sensor values 50 cm
The 50cm values could be
ir 0.496 0.426 4633 4761 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.500 0.426 4600 4770 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.496 0.426 4628 4764 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.494 0.426 4641 4762 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.498 0.426 4616 4761 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.496 0.427 4627 4759 15000 4600 15000 4100 1 ir 0.481 0.427 4741 4756 15000 4600 15000 4100 1
The value seems fine for sensor 1 (default side-mounted); it is a bit off for the other sensor.
Implement calibration
To implement the new calibration values, use (in this case).
- Help text is: irc A1 B1 A2 B2 V Set calibration values A=13cm value, B=50cm (sensor 1 and 2) V=1 in on.
irc 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 or MQTT, publish: topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message: "irc 15660 4600 14210 4760 1"
Then save to the Teensy flash:
eew or using MQTT topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message "eew"
The values at 50cm now look like:
ir 0.501 0.501 4590 4756 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 ir 0.491 0.498 4669 4770 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 ir 0.498 0.501 4619 4754 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 ir 0.499 0.499 4610 4765 15660 4600 14210 4760 1 ir 0.493 0.501 4654 4755 15660 4600 14210 4760 1
After this calibration, the actual values should be within 3-5 cm in the 10cm to 50cm range.
Reflections
If the sensor looks into a reflecting surface, then this may disturb the reading.
Back to normal
The teensy_interface was terminated, and further, the CRC was disabled.
Turn on CRC:
echo "i 0" >/dev/ttyACM0
Restart the teensy_interface, or maybe better, reboot the Raspberry:
sudo reboot now
alternatively, restart
cd ~/svn/robobot/teensy_interface/build ./teensy_interface -l
But the restarted process will be terminated sometime after you terminate the command line access.
Calibrate odometry
Robot wheel configuration requires:
- Wheel radius (around 7.5cm)
- Gear ratio (19:1)
- Encoder ticks per revolution (92)
- Distance between wheels (around 23cm)
These values are sent to the teensy_firmware_8 as confw rl rr gear TPR wb, e.g.:
confw 0.0750 0.0750 19 92 0.234 or using MQTT topic: robobot/cmd/T0 message: "confw 0.0750 0.0750 19 92 0.234"
The values can be queried with a configi command, which returns, e.g.:
conf 0.0750 0.0750 19.000 92 0.2340 0.0020 0 or, if subscribed from MQTT topic: robobot/drive/T0 message: conf 0.0750 0.0750 19.000 92 0.2340 0.0020 0
The last 0.0020 is the system sample time, here 2ms. The last 0 is for motortest only.
The simple method is:
- Order the robot to drive 1m, check how long the robot thinks it has driven, e.g. 1.02m, then compare with reality, and adjust the wheel radius as relevant.
- Order the robot to turn, e.g. 180 degrees, compare with reality and adjust the distance between driving wheels as needed.