Robobot circuits: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Figure 3. The Regbot circuit. | Figure 3. The Regbot circuit. | ||
=== PCB | === PCB === | ||
[[File: | [[File:PCB_layout_8.5.png | 900px]] | ||
Figure 5. PCB with more trace details. | |||
=== PCB - 3D view === | |||
[[File: | [[File:PCB_foto_8.5.jpg | 900px]] | ||
Figure | Figure 4. Populated PCB. | ||
== Line sensor == | == Line sensor == | ||
Revision as of 16:51, 27 December 2024
Back to Robobot_B
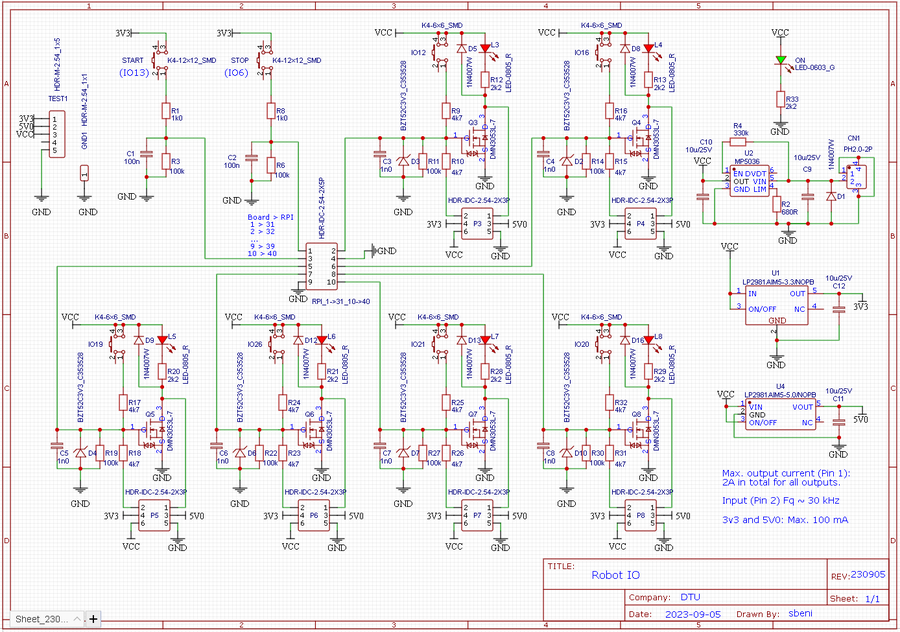
Digital IO
Circuit diagram
Figure 1. The circuit diagram should ensure that each IO pin can function as both input and output. If input, then the pin has active pull down, i.e. for input to change, it must be pulled high, to at least 3.3V, but 5 or 12V will work too. If output, then a transistor is active when output is high, and can draw at least 1A from the 12V supply. The 5V and 3.3V can supply no more than 100mA.
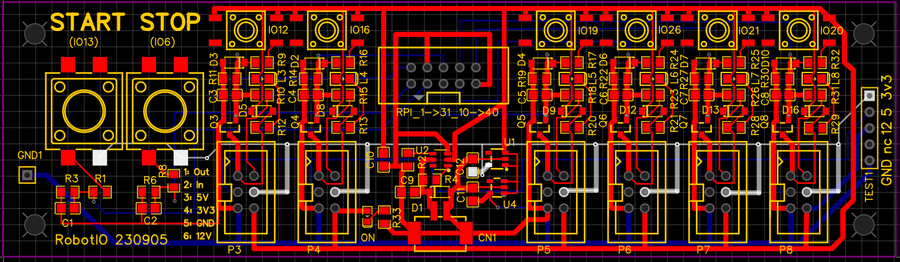
PCB
Figure 2. The PCB layout for the digital IO circuit.
Regbot
Circuit diagram
Figure 3. The Regbot circuit.
PCB
Figure 5. PCB with more trace details.
PCB - 3D view
Figure 4. Populated PCB.
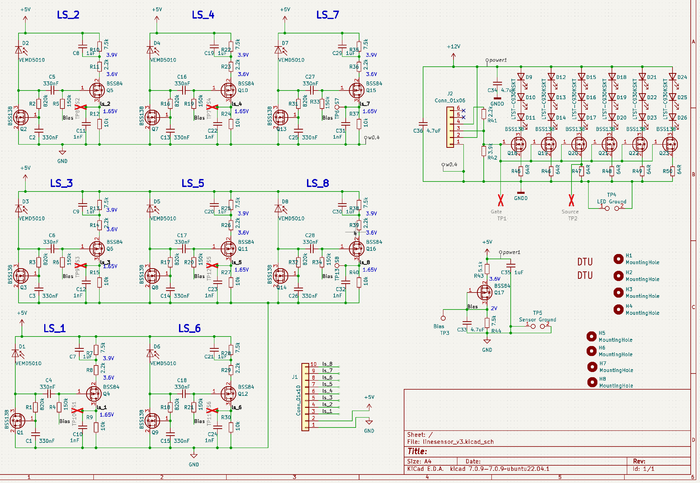
Line sensor
Circuit
Figure 6. Circuit diagram for the line sensor. 8 sensors with a change amplifier and analog output. The 18 LEDs provides the blinking light (1kHz).
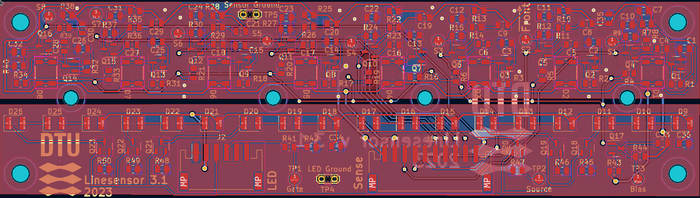
PCB
Figure 7. The PCB in 3D view. The distance from the first to the last sensor is 12cm.
Figure 8. PCB layout.
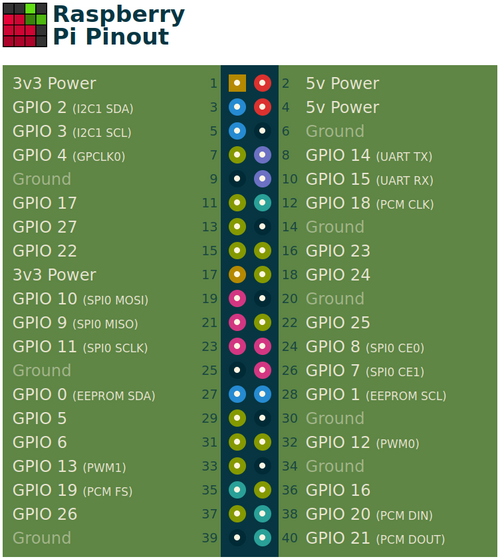
Raspberry PI
Figure 9. GPIO pin numbers.