Robobot teensy interface: Difference between revisions
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
topic: ''robobot/drive/T0/liv'' | topic: ''robobot/drive/T0/liv'' | ||
message: ''731 928 962 866 888 902 828 613 50'' | message: ''1736776814.3819 731 928 962 866 888 902 828 613 50'' | ||
The first part of the topic, ''robobot/drive/T0'', is the same for all messages from the Teensy. | The first part of the topic, ''robobot/drive/T0'', is the same for all messages from the Teensy. | ||
If you want to subscribe to all MQTT messages, the topic request could be ''robobot/drive/#.'' | If you want to subscribe to all MQTT messages, the topic request could be ''robobot/drive/#.'' | ||
The message is preceded by a timestamp, which is when the message was received from Teensy. The timestamp is seconds from the start of the epoch (1 Jan 1970) that is standard for all PCs | |||
=== Data extract === | |||
The most relevant data is decoded in the interface and, in some cases, slightly reformatted before being sent to MQTT. | |||
The decoded data can further be saved to individual logfiles. | |||
=== Motor control === | |||
Motor control translated drive command, linear velocity (m/s) and rotation speed (rad/s), into motor voltage sent to the Teensy. | |||
The ''mixer'' module calculates each wheel's needed velocity to satisfy the drive command. | |||
The ''motor'' module uses a closed loop control to implement wheel velocity. The controller is a PID type. The parameters are configured in the ''robot.ini'' file. The measured velocity is taken from the ''velocity'' data module. | |||
=== Gamepad control === | |||
There is an optional possibility of controlling the robot from a gamepad (Logitech is supported only). | |||
The manual control takes over when the ''back'' button on the gamepad is pressed. | |||
=== Configuration file === | |||
All modules are configured by the settings in the ''robot.ini'' file. Especially: | |||
* data subscription from the Teensy for essential data (like wheel velocity) | |||
* Wheel size and other static configuration data | |||
* Logfile settings | |||
Revision as of 09:54, 18 January 2025
Back to Robobot_B
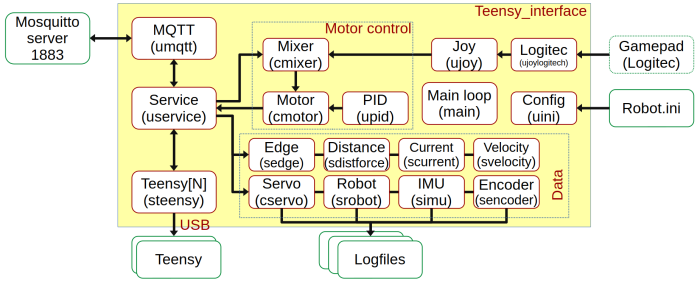
Teensy interface
The Teensy_interface app has the functions:
- Translate between the USB connection and the MQTT protocol.
- Adds motor velocity control (allow control using linear velocity and rotation velocity)
- Allow log of almost all relevant data to individual logfiles. Intended for debugging and import into Matlab.
- Monitors the IP addresses of the Raspberry and sends the result to the small Teensy display.
The app is configured with the file robot.ini
Teensy to MQTT
The teensy_interface app can interface with more than one Teensy, but for Robobot, only one Teensy board is available.
The Teensy data can be converted to an MQTT message directly, which is the default method.
The Teensy data message for raw line-sensor AD values has the format.:
liv 731 928 962 866 888 902 828 613 50
This will, in MQTT, be split into a topic and a message.
topic: robobot/drive/T0/liv message: 1736776814.3819 731 928 962 866 888 902 828 613 50
The first part of the topic, robobot/drive/T0, is the same for all messages from the Teensy.
If you want to subscribe to all MQTT messages, the topic request could be robobot/drive/#.
The message is preceded by a timestamp, which is when the message was received from Teensy. The timestamp is seconds from the start of the epoch (1 Jan 1970) that is standard for all PCs
Data extract
The most relevant data is decoded in the interface and, in some cases, slightly reformatted before being sent to MQTT.
The decoded data can further be saved to individual logfiles.
Motor control
Motor control translated drive command, linear velocity (m/s) and rotation speed (rad/s), into motor voltage sent to the Teensy.
The mixer module calculates each wheel's needed velocity to satisfy the drive command.
The motor module uses a closed loop control to implement wheel velocity. The controller is a PID type. The parameters are configured in the robot.ini file. The measured velocity is taken from the velocity data module.
Gamepad control
There is an optional possibility of controlling the robot from a gamepad (Logitech is supported only).
The manual control takes over when the back button on the gamepad is pressed.
Configuration file
All modules are configured by the settings in the robot.ini file. Especially:
- data subscription from the Teensy for essential data (like wheel velocity)
- Wheel size and other static configuration data
- Logfile settings