Robobot MQTT-client: Difference between revisions
(→Log) |
(→Camera) |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
A small example of using openCV to manipulate image frames is included. | A small example of using openCV to manipulate image frames is included. | ||
@todo camera image annotated | |||
=== GPIO === | === GPIO === | ||
Revision as of 19:13, 18 January 2025
Back to Robobot_B
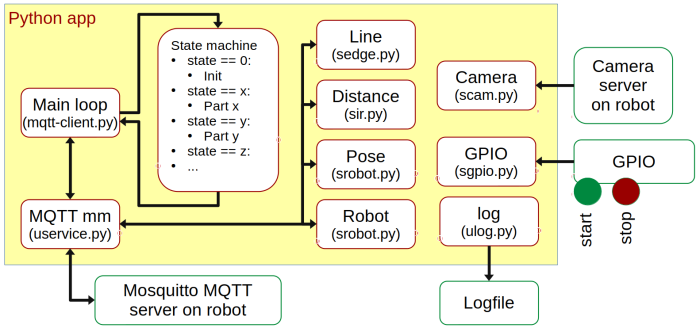
MQTT-client in Python
This skeleton is intended as the mission controller app.
mqtt-client.py
This is the primary file in the mission control skeleton.
It is intended to run on the Raspberry Pi, using the command:
cd ~/svn/robobot/mqtt_python python3 mqtt-client.py
All the interfaces have a network interface except the GPIO (General Purpose Input Output). This allows the app to run anywhere with network access to the robot.
Command line parameters
The app has defined a few command line parameters, among these help:
python3 mqtt-client.py --help % Starting usage: mqtt-client.py [-h] [-w] [-g] [-l] [-s] [-n] Robobot app 2024 options: -h, --help show this help message and exit -w, --white Calibrate white tape level -g, --gyro Calibrate gyro -l, --level Calibrate horizontal -s, --silent Print less to console -n, --now Start drive now (do not wait for start button)
The command line options include some sensor calibration. The distance sensor calibration is missing (but needed).
Main loop
The
MQTT service
This module handles the MQTT communication.
Robot
This module decodes some of the robot's basic data, e.g., battery voltage.
All the data interfaces have an update counter that estimates the interval between updates. This is intended as a debug measure to detect potential slow network situations.
Pose
The robot pose has data related to the robot's movement.
The data is provided by requesting configuration data directly from Teensy and listening to the data streams configured by the teensy_interface.
The streamed data is
- Wheel velocity (message topic robobot/drive/T0/vel) in m/s.
- Motor velocity (message topic robobot/drive/T0/mvel) before the gear. The unit is radians/sec. This stream is probably not needed.
- The robot pose (message topic robobot/drive/T0/pose) is the x,y position and the robot heading as calculated in the Teensy.
Distance
The IR distances are received from Teensy and should be in meters, but this requires some calibration.
The distance sensor can give unreliable values if the infrared beam is not reflected within about 1m. This is why the sensor's default position points slightly down towards the floor.
Line
The line sensor has 8 reflection channels. This module receives a data stream with normalized values (assuming the sensor is calibrated).
Calibration on a white line is needed and can be done with a command line option.
There is a tape line position estimator in this module. It is based on an average calculation and is probably not good to follow a line edge in junctions.
Camera
The camera module captures images from the camera server stream.
The server sets the resolution and framerate.
A small example of using openCV to manipulate image frames is included.
@todo camera image annotated
GPIO
Eight of the Raspberry Pi pins are available as general-purpose input-output. Two are dedicated as start and stop buttons.
The GPIO board has drivers capable of driving a high current (pull a relay or similar).
A button is available on all lines to give a signal to an input line and to simulate an output line.
See the circuit diagram for the IO board here Robobot circuits.
Log
A simple logging module is provided. The intention is to make a file with essential data that can be used for Matlab plotting.
The first lines are intended to describe the data columns. They are preceded by a "%" that will be seen as a comment by Matlab.
Remarks, like state change, can be added, and will be saved in the file with the "%" and a timestamp.
@todo example